<InfiniteListBase>
The <InfiniteListBase> component is a headless version of the infinite list functionality. It fetches records from the data provider and provides infinite scrolling capabilities through a ListContext, but doesn’t render any UI by itself. This allows you to create fully custom list layouts with infinite loading.
<InfiniteListBase> fetches the list of records from the data provider using the useInfiniteListController hook and provides the data through a context. You have complete control over how to render the list of records.
Here is the minimal code necessary to display a list of books with infinite scroll:
// in src/books.jsimport { InfiniteListBase, useListContext, useInfinitePaginationContext } from 'ra-core';
const BookTable = () => { const { data, isPending } = useListContext();
if (isPending) { return <div>Loading...</div>; }
return ( <table> <thead> <tr> <th>ID</th> <th>Title</th> <th>Author</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> {data.map(book => ( <tr key={book.id}> <td>{book.id}</td> <td>{book.title}</td> <td>{book.author}</td> </tr> ))} </tbody> </table> );};
const InfinitePagination = () => { const { hasNextPage, fetchNextPage, isFetchingNextPage } = useInfinitePaginationContext();
if (!hasNextPage) { return null; }
return ( <div style={{ textAlign: 'center', margin: '1rem' }}> <button disabled={isFetchingNextPage} onClick={() => fetchNextPage()} > {isFetchingNextPage ? 'Loading...' : 'Load more'} </button> </div> );};
export const BookList = () => ( <InfiniteListBase> <div> <h1>Books</h1> <BookTable /> <InfinitePagination /> </div> </InfiniteListBase>);
// in src/App.jsimport { CoreAdmin, Resource } from 'ra-core';import jsonServerProvider from 'ra-data-json-server';
import { BookList } from './books';
const App = () => ( <CoreAdmin dataProvider={jsonServerProvider('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com')}> <Resource name="books" list={BookList} /> </CoreAdmin>);
export default App;That’s enough to display a basic list with infinite scroll functionality. When users click the “Load more” button, additional records are fetched and appended to the list.
<InfiniteListBase> accepts the same props as <ListBase>, but configured for infinite loading:
| Prop | Required | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
authLoading | Optional | ReactNode | - | The component to render while checking for authentication and permissions. |
children | Required if no render | ReactNode | - | The component to use to render the list of records. |
render | Required if no children | ReactNode | - | A function that render the list of records, receives the list context as argument. |
debounce | Optional | number | 500 | The debounce delay in milliseconds to apply when users change the sort or filter parameters. |
disable Authentication | Optional | boolean | false | Set to true to disable the authentication check. |
disable SyncWithLocation | Optional | boolean | false | Set to true to disable the synchronization of the list parameters with the URL. |
empty | Optional | ReactNode | - | The component to display when the list is empty. |
emptyWhileLoading | Optional | boolean | - | Set to true to return null while the list is loading. |
error | Optional | ReactNode | - | The component to render when failing to load the list of records. |
exporter | Optional | function | - | The function to call to export the list. |
filter | Optional | object | - | The permanent filter values. |
filter DefaultValues | Optional | object | - | The default filter values. |
loading | Optional | ReactNode | - | The component to render while loading the list of records. |
perPage | Optional | number | 10 | The number of records to fetch per page. |
queryOptions | Optional | object | - | The options to pass to the useQuery hook. |
resource | Optional | string | - | The resource name, e.g. posts. |
sort | Optional | object | - | The initial sort parameters. |
storeKey | Optional | string | - | The key to use to store the current filter & sort. |
Check the <ListBase> component for details about each prop.
Pagination
Section titled “Pagination”Since <InfiniteListBase> is headless, you need to implement your own pagination component. You can use the useInfinitePaginationContext hook to get the pagination state and callbacks.
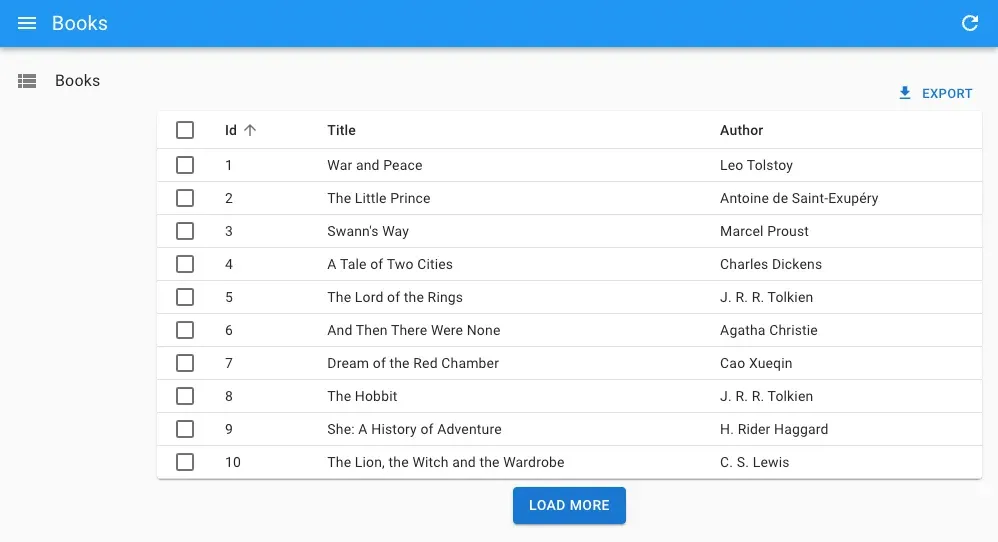
For example, here is a custom infinite pagination component displaying a “Load More” button at the bottom of the list:
import { InfiniteListBase, useInfinitePaginationContext, useListContext } from 'ra-core';
const LoadMore = () => { const { hasNextPage, fetchNextPage, isFetchingNextPage, } = useInfinitePaginationContext();
return hasNextPage ? ( <div style={{ marginTop: '1rem', textAlign: "center" }}> <button disabled={isFetchingNextPage} onClick={() => fetchNextPage()} > Load more </button> </div> ) : null;};
const BookTable = () => { const { data } = useListContext();
return ( <table> <thead> <tr> <th>ID</th> <th>Title</th> <th>Author</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> {data.map(book => ( <tr key={book.id}> <td>{book.id}</td> <td>{book.title}</td> <td>{book.author}</td> </tr> ))} </tbody> </table> );};
export const BookList = () => ( <InfiniteListBase> <div> <BookTable /> <LoadMore /> </div> </InfiniteListBase>);Showing The Record Count
Section titled “Showing The Record Count”You can use useListContext to access the total property of the list, and render the total number of results in a sticky footer:
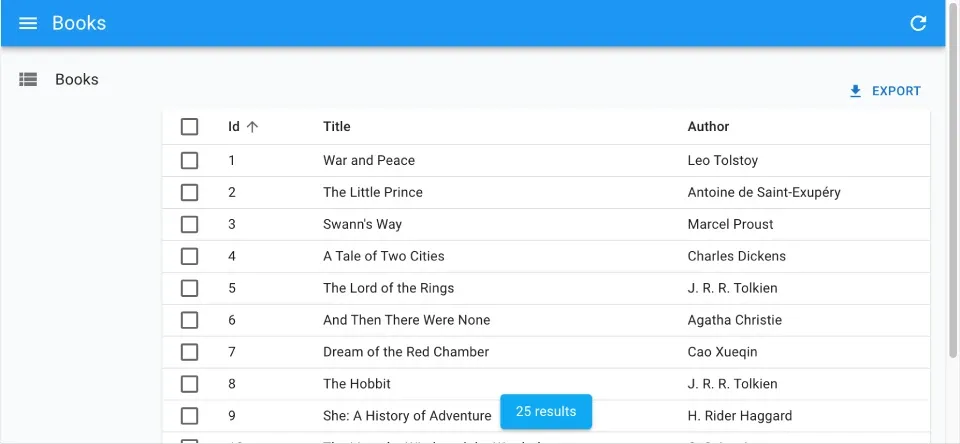
import { useListContext, useInfinitePaginationContext, InfiniteListBase } from 'ra-core';
const CustomPagination = () => { const { total } = useListContext(); const { hasNextPage, fetchNextPage, isFetchingNextPage } = useInfinitePaginationContext();
return ( <div> {hasNextPage && ( <div style={{ textAlign: 'center', margin: '1rem' }}> <button disabled={isFetchingNextPage} onClick={() => fetchNextPage()} > {isFetchingNextPage ? 'Loading...' : 'Load more'} </button> </div> )} {total > 0 && ( <div style={{ position: "sticky", bottom: 0, textAlign: "center", backgroundColor: 'white', border: '1px solid #ccc', padding: '0.5rem', margin: '0.5rem', borderRadius: '4px' }}> <span>{total} results</span> </div> )} </div> );};
export const BookList = () => ( <InfiniteListBase> <div> {/* Your list content here */} <CustomPagination /> </div> </InfiniteListBase>);Controlled Mode
Section titled “Controlled Mode”<InfiniteListBase> deduces the resource and the list parameters from the URL. This is fine for a page showing a single list of records, but if you need to display more than one list in a page, you probably want to define the list parameters yourself.
In that case, use the resource, sort, and filter props to set the list parameters.
import { InfiniteListBase, useListContext, useInfinitePaginationContext } from 'ra-core';
const SimpleList = ({ primaryText, secondaryText, tertiaryText }) => { const { data } = useListContext();
return ( <div> {data.map(item => ( <div key={item.id} style={{ padding: '1rem', borderBottom: '1px solid #eee' }}> <div style={{ fontWeight: 'bold' }}> {primaryText(item)} </div> {secondaryText && ( <div style={{ color: '#666' }}> {secondaryText(item)} </div> )} {tertiaryText && ( <div style={{ fontSize: '0.875rem', color: '#999' }}> {tertiaryText(item)} </div> )} </div> ))} </div> );};
const InfinitePagination = () => { const { hasNextPage, fetchNextPage, isFetchingNextPage } = useInfinitePaginationContext();
return hasNextPage ? ( <div style={{ textAlign: 'center', margin: '1rem' }}> <button disabled={isFetchingNextPage} onClick={() => fetchNextPage()} > {isFetchingNextPage ? 'Loading...' : 'Load more'} </button> </div> ) : null;};
const Dashboard = () => ( <div style={{ padding: '2rem' }}> <h2>Latest posts</h2> <InfiniteListBase resource="posts" sort={{ field: 'published_at', order: 'DESC' }} filter={{ is_published: true }} disableSyncWithLocation > <SimpleList primaryText={record => record.title} secondaryText={record => `${record.views} views`} /> <InfinitePagination /> </InfiniteListBase>
<h2>Latest comments</h2> <InfiniteListBase resource="comments" sort={{ field: 'published_at', order: 'DESC' }} perPage={10} disableSyncWithLocation > <SimpleList primaryText={record => record.author.name} secondaryText={record => record.body} tertiaryText={record => new Date(record.published_at).toLocaleDateString()} /> <InfinitePagination /> </InfiniteListBase> </div>)Using the Hook Directly
Section titled “Using the Hook Directly”If you don’t need the ListContext, you can use the useInfiniteListController hook directly, which does the same data fetching as <InfiniteListBase> but lets you render the content however you want.
import { useInfiniteListController } from 'ra-core';
const ProductList = () => { const { isPending, data, hasNextPage, fetchNextPage, isFetchingNextPage } = useInfiniteListController({ resource: 'products' });
return ( <div style={{ padding: '2rem' }}> <h1>All products</h1> {!isPending && ( <div style={{ display: 'flex', flexDirection: 'column', gap: '1rem' }}> {data.map(product => ( <div key={product.id} style={{ border: '1px solid #ccc', padding: '1rem', borderRadius: '4px' }}> <h3>{product.name}</h3> </div> ))} </div> )} {hasNextPage && ( <div style={{ textAlign: 'center', marginTop: '2rem' }}> <button disabled={isFetchingNextPage} onClick={() => fetchNextPage()} > {isFetchingNextPage ? 'Loading...' : 'Load more'} </button> </div> )} </div> );};useInfiniteListController returns callbacks to sort, filter, and paginate the list, so you can build a complete infinite list page.
Security
Section titled “Security”The <InfiniteListBase> component requires authentication and will redirect anonymous users to the login page. If you want to allow anonymous access, use the disableAuthentication prop.
If your authProvider implements Access Control, <InfiniteListBase> will only render if the user has the “list” access to the related resource.
For instance, for the <PostList> page below:
import { InfiniteListBase, useListContext } from 'ra-core';
const PostTable = () => { const { data } = useListContext();
return ( <table> <thead> <tr> <th>Title</th> <th>Author</th> <th>Published At</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> {data.map(post => ( <tr key={post.id}> <td>{post.title}</td> <td>{post.author}</td> <td>{post.published_at}</td> </tr> ))} </tbody> </table> );};
// Resource name is "posts"const PostList = () => ( <InfiniteListBase> <PostTable /> </InfiniteListBase>);<InfiniteListBase> will call authProvider.canAccess() using the following parameters:
{ action: "list", resource: "posts" }Users without access will be redirected to the Access Denied page.
Note: Access control is disabled when you use the disableAuthentication prop.