Getting Started
Atomic CRM is designed to be easy to customize and extend by developers with basic React and SQL skills. This guide will help you get started with installing, configuring, and deploying Atomic CRM.
Prerequisites
Section titled “Prerequisites”- A GitHub account
- Git
- Node.js (version 20 or higher)
- Docker
- A Supabase account for production deployment
Installation
Section titled “Installation”-
Fork the Atomic CRM repository on GitHub to your own account.
-
Clone your forked repository to your local machine:
Terminal window git clone https://github.com/[username]/atomic-crm.gitcd atomic-crm -
Install the dependencies:
Terminal window npm install
Running Locally
Section titled “Running Locally”-
Start the database and API, powered by Supabase:
Terminal window npx supabase start -
Start the development server, powered by Vite:
Terminal window npm run dev
Atomic CRM now runs at http://localhost:5173/.
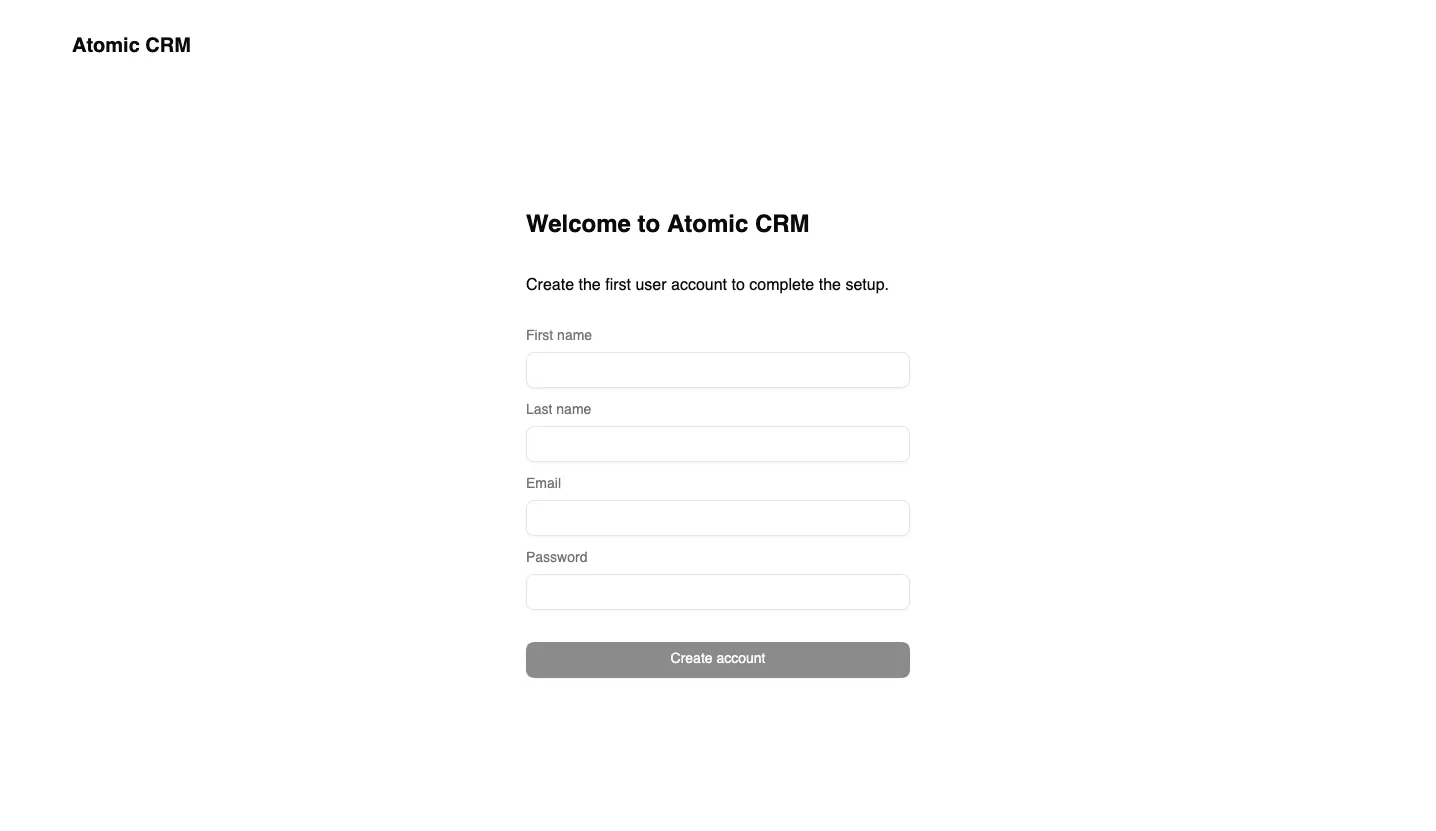
Admin User Setup
Section titled “Admin User Setup”When you first access the application at http://localhost:5173/, you will be prompted to create the first admin user. This user will have full access to the application and will be able to manage other users.
Once the admin user is created, you will be redirected to the dashboard. It’s currently showing an onboarding screen to help you get started as long as there is no data in the database.
Bootstrapping with Sample Data
Section titled “Bootstrapping with Sample Data”It’s easier to develop on a non-empty application. Atomic CRM provides a sample dataset you can import to get started. Click the import button and choose the sample data file at test-data/contacts.csv. This will add 500 contacts and 55 companies to your local database.
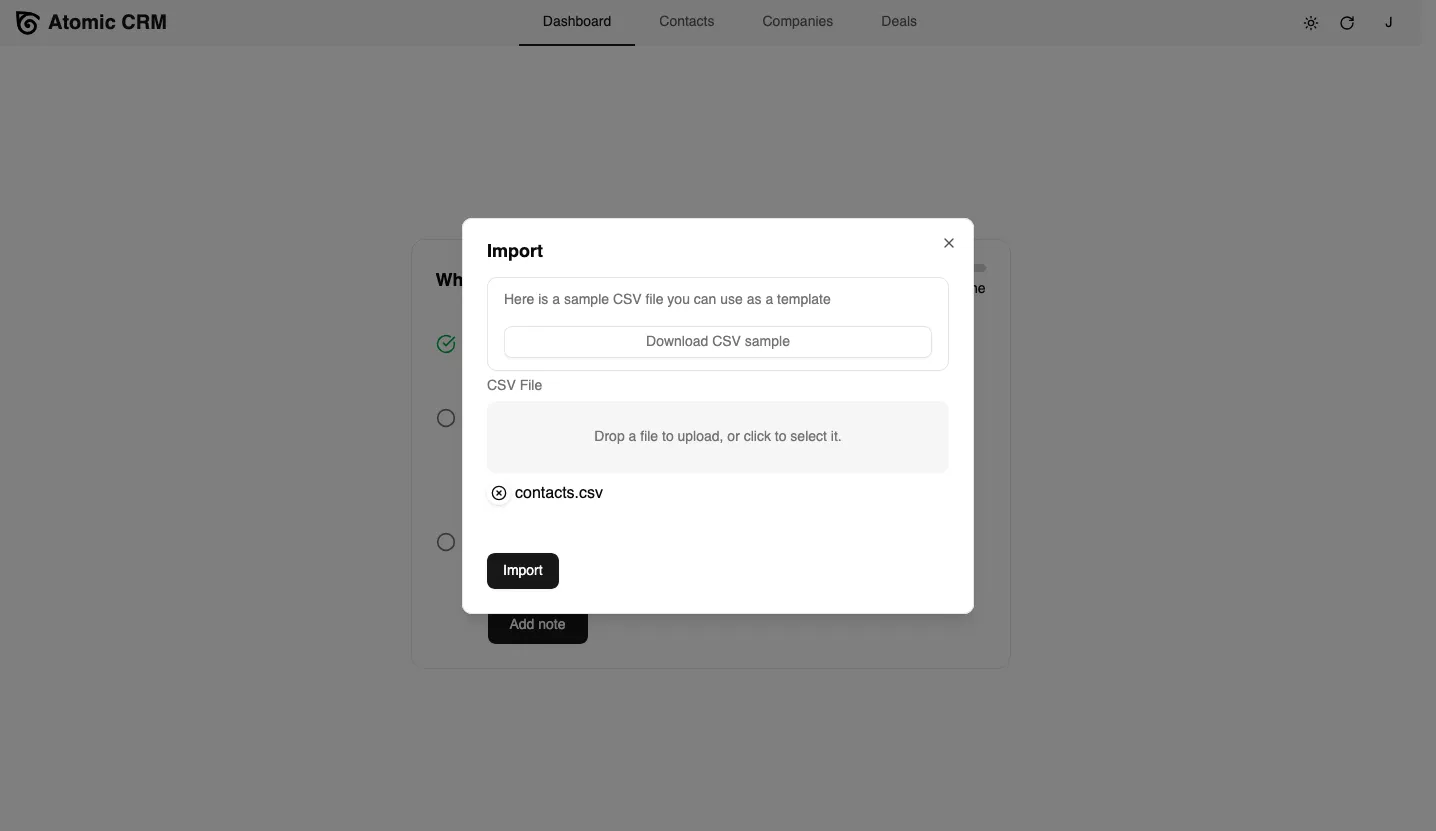
Now you can navigate to the Contacts list. Play with the application to get familiar with its features. Add a few notes and tasks to some contacts. This will end the onboarding and reveal the regular dashboard.
Configuring the Application
Section titled “Configuring the Application”The entry point of the application is the src/App.tsx file. By default, this file simply renders the <CRM> component, which is the root component of Atomic CRM.
import { CRM } from "@/components/atomic-crm/root/CRM";
const App = () => <CRM />;
export default App;<CRM> accepts various props to customize the application domain and look and feel. For instance, the following code snippet shows how to customize the app title, the task types, and deal categories.
import { CRM } from "@/components/atomic-crm/root/CRM";
const App = () => ( <CRM title="Acme CRM" taskTypes={[ { value: 'call', label: 'Call' }, { value: 'email', label: 'Email' }, { value: 'meeting', label: 'Meeting' }, ]} dealCategories={[ { value: 'ecommerce', label: 'eCommerce' }, { value: 'saas', label: 'SaaS' }, { value: 'consulting', label: 'Consulting' }, ]} />);
export default App;
Check the Customizing Atomic CRM guide for an exhaustive list of configuration settings you can customize.
Adding Custom Fields
Section titled “Adding Custom Fields”You can extend the data model of Atomic CRM by adding custom fields to the existing entities (Contacts, Companies, Deals, Notes, and Tasks).
You will do so in the Supabase Studio. To access the Studio, go to http://localhost:54323/.
We’re going to add a custom field to the Contacts table: a “Referred By” text field to store the name of the person who referred the contact.
-
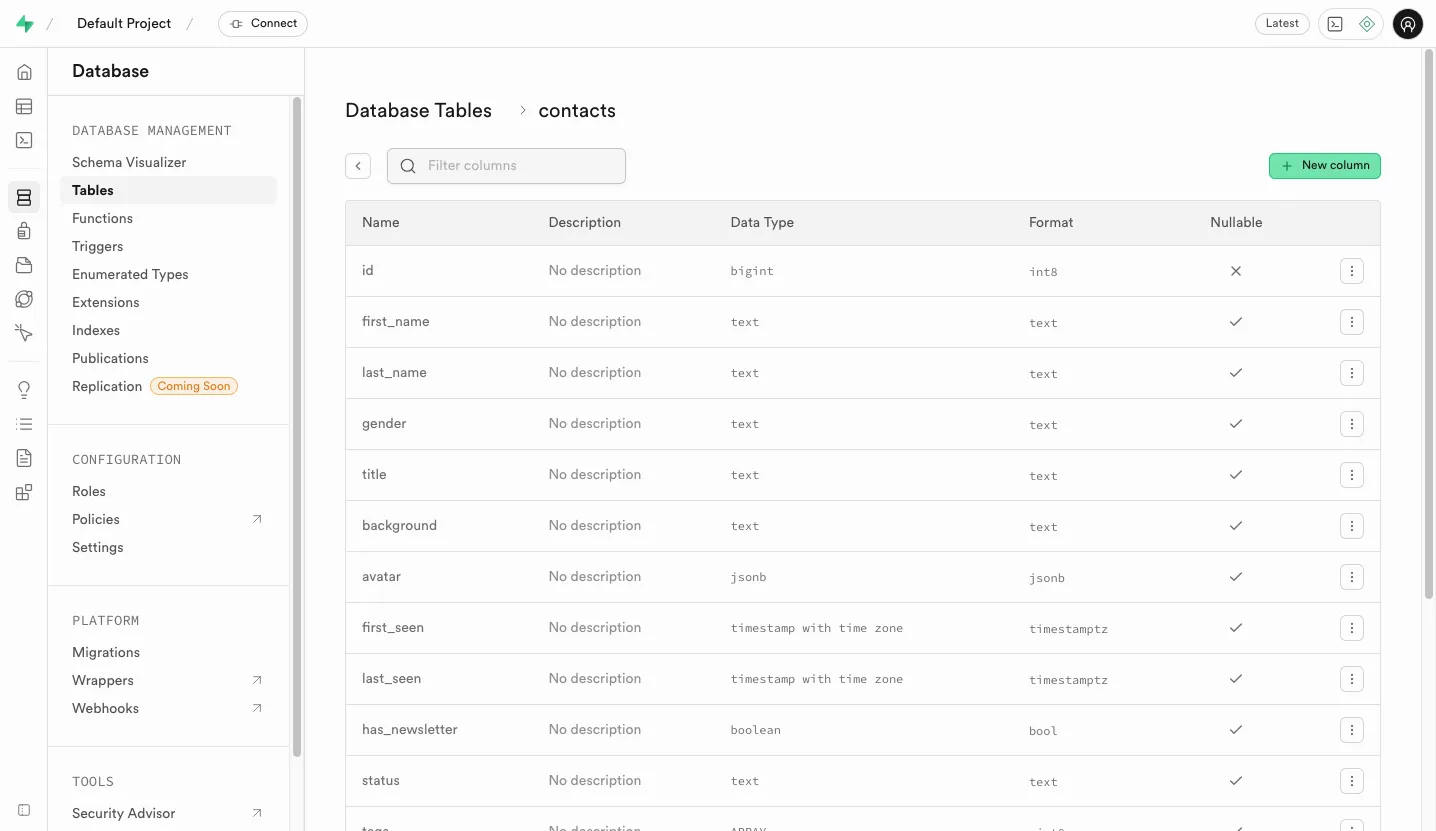
Click on the Database menu
-
Choose the Tables section in the Database management panel. You will see the list of tables used by Atomic CRM.
-
Click on the
contactstable in the list of tables. -
Click on the “New Column” button to add a new column to the table.
-
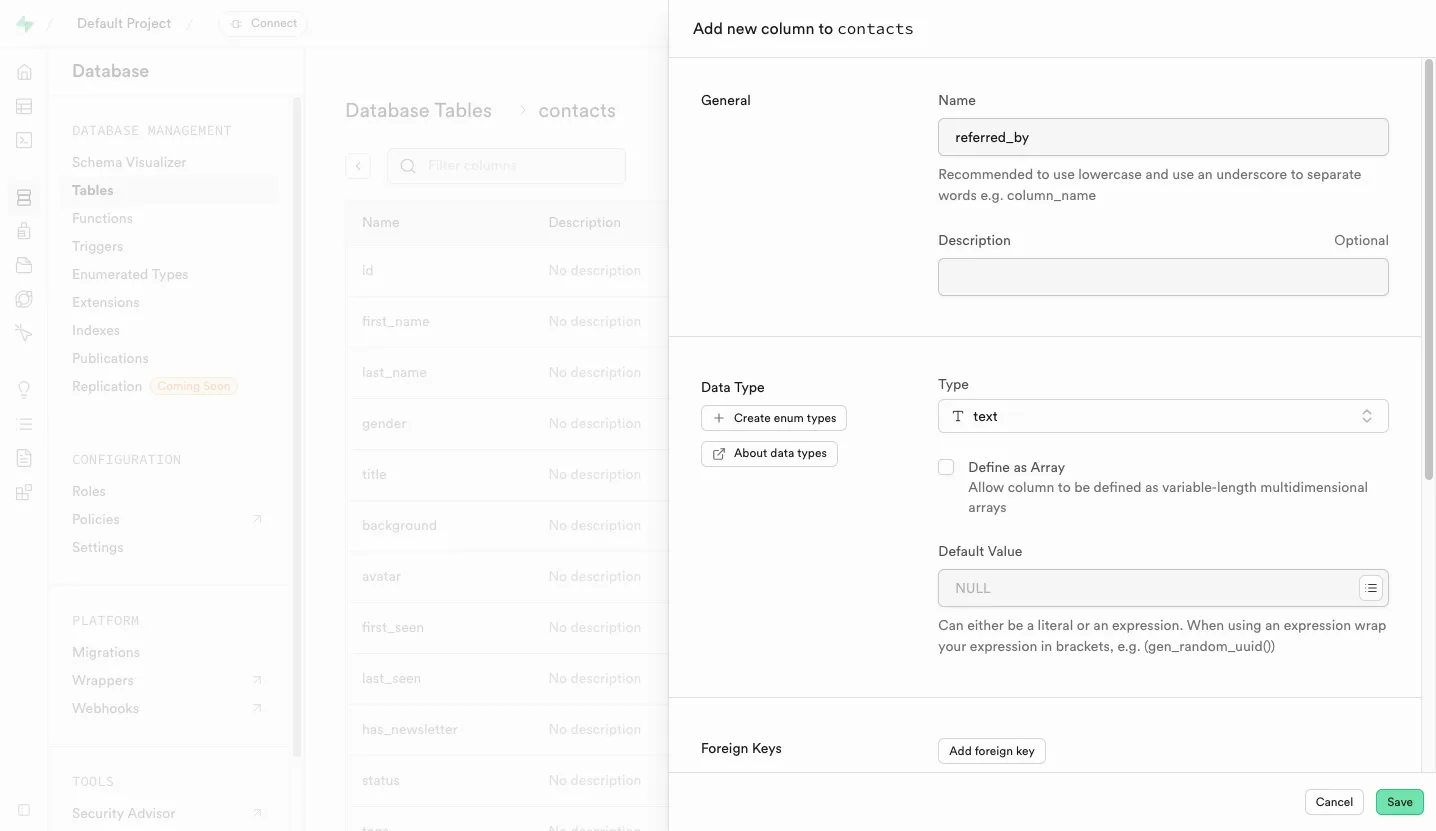
In the “Add new column to contacts” dialog, enter the following details:
- Name:
referred_by - Type:
text - Default value: leave empty
- Allow Nullable: checked
- Name:
-
Finally, click on the “Save” button to add the new column to the table.
Atomic CRM uses views to simplify the queries. You need to update the contacts_summary view to include the new referred_by field.
-
Click on the “SQL Editor” menu in the left sidebar.
-
Enter the following SQL query to update the
contacts_summaryview:drop view "public"."contacts_summary";create view "public"."contacts_summary"with (security_invoker=on)asselectco.*,c.name as company_name,count(distinct t.id) as nb_tasksfrom"public"."contacts" coleft join"public"."tasks" t on co.id = t.contact_idleft join"public"."companies" c on co.company_id = c.idgroup byco.id, c.name;
-
Click on the “Run” button to execute the SQL command. You will need to confirm the action since it will drop and recreate the view.
-
Create a migration for these schema changes, to allow them to be replicated in production. Run the following command in your terminal:
Terminal window npx supabase db diff -f create_referred_byThis will create a new migration file in the
supabase/migrationsfolder. Supabase will automatically apply this migration when you deploy to production.
That’s it! You’ve just added a custom field to the Contacts entity. Supabase automatically updates the API to include the new field.
Displaying Custom Fields in the Frontend
Section titled “Displaying Custom Fields in the Frontend”Next, you need to make this new field available in the frontend.
The frontend code lives in the src/components/atomic-crm folder, and is organized by entities. Each entity has its own folder containing all the components related to that entity. Take a few minutes to explore the codebase and familiarize yourself with its structure.
Atomic CRM uses TypeScript to ensure type safety, so you’ll need to modify the Contact type to include the new referred_by field. Open the src/components/atomic-crm/types.ts file and add the referred_by field to the Contact interface.
export type Contact = { first_name: string; last_name: string; title: string; company_id: Identifier; email_jsonb: EmailAndType[]; avatar?: Partial<RAFile>; linkedin_url?: string | null; first_seen: string; last_seen: string; has_newsletter: boolean; tags: Identifier[]; gender: string; sales_id: Identifier; status: string; background: string; phone_jsonb: PhoneNumberAndType[]; referred_by?: string; nb_tasks?: number; company_name?: string;} & Pick<RaRecord, "id">;You will modify the contact creation and edition form to include an input for the referred_by field.
To do so, open the src/components/atomic-crm/contacts/ContactInputs.tsx file to edit the <ContactInputs> component and add a new <TextInput>.
const ContactMiscInputs = () => { return ( <div className="flex flex-col gap-4"> <h6 className="text-lg font-semibold">Misc</h6> <TextInput source="referred_by" helperText={false} /> <TextInput source="background" label="Background info (bio, how you met, etc)" multiline helperText={false} /> <BooleanInput source="has_newsletter" helperText={false} /> <ReferenceInput reference="sales" source="sales_id" sort={{ field: "last_name", order: "ASC" }} filter={{ "disabled@neq": true, }} > <SelectInput helperText={false} label="Account manager" optionText={saleOptionRenderer} validate={required()} /> </ReferenceInput> </div> );};<TextInput> is a Shadcn Admin Kit component that binds a form field to the form state. Upon submission, the form data will include the referred_by field and the Supabase API will store it in the database.
The application will automatically pick up this code change. Go back to http://localhost:5173/ and you can now create or edit a contact and set the “Referred By” field.
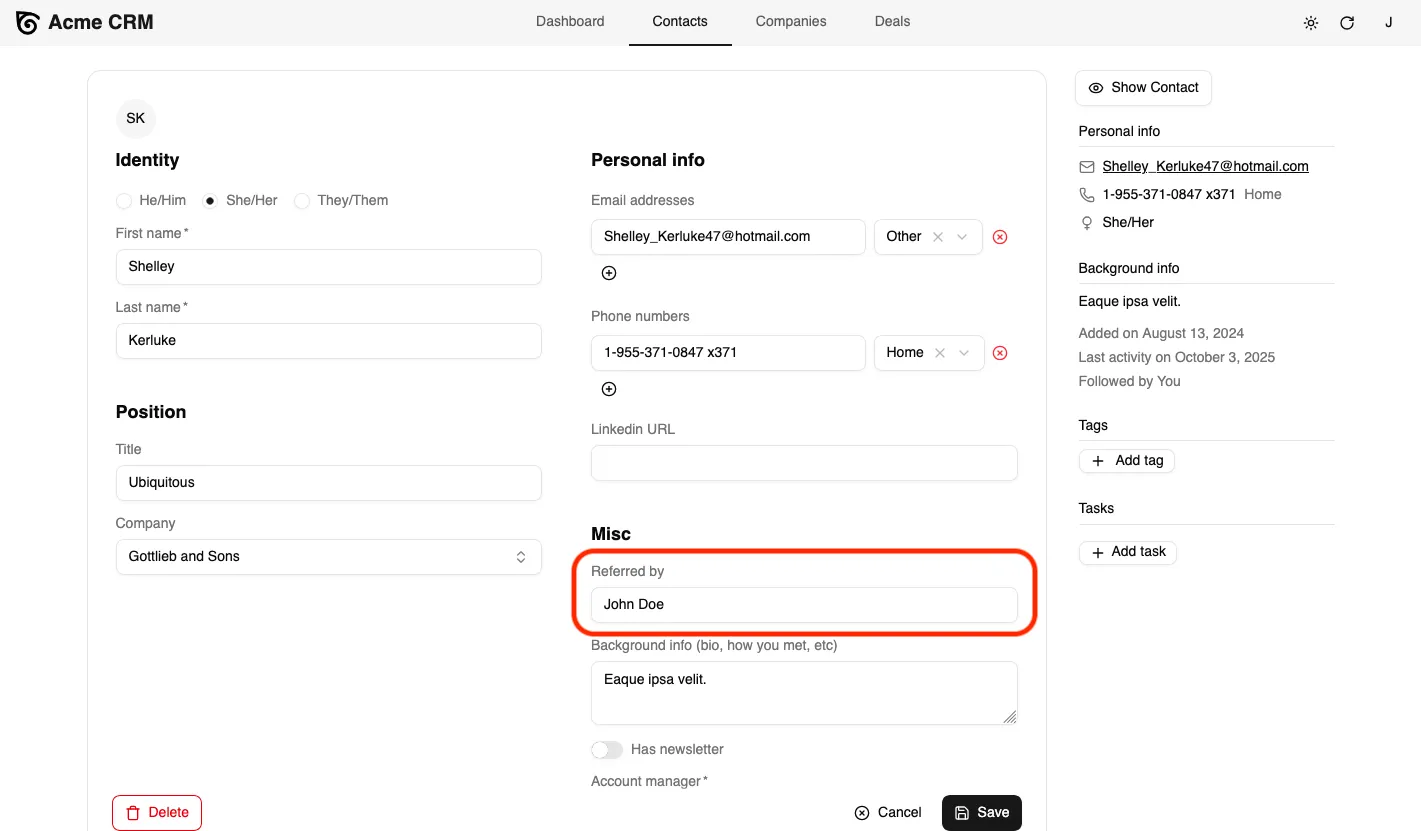
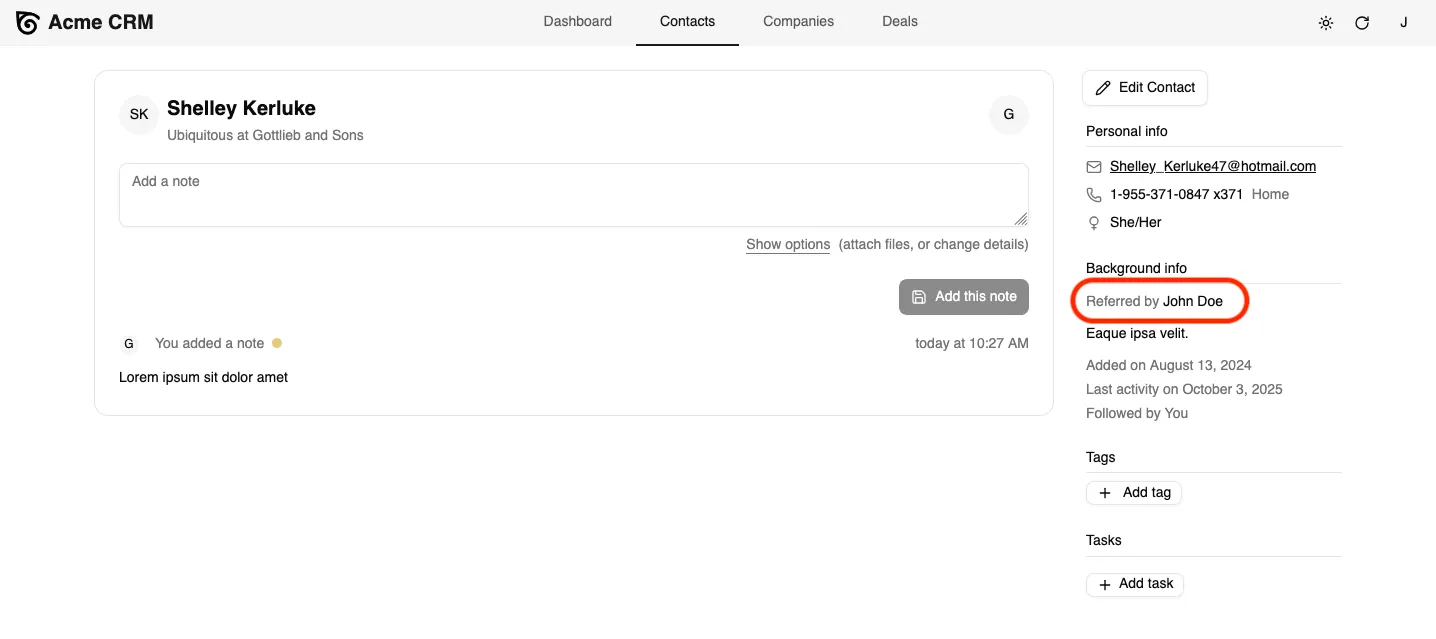
Finally, update the Contacts sidebar to display the referrer when available. Open the src/components/atomic-crm/contacts/ContactAside.tsx file and add a new <TextField> for the referred_by field.
export const ContactAside = ({ link = "edit" }: { link?: "edit" | "show" }) => { // ... <AsideSection title="Background info"> {record.referred_by && ( <div className="pb-2"> <span className="text-sm text-muted-foreground mr-1"> Referred by </span> <TextField source="referred_by" /> </div> )} <WithRecord<Contact> render={(record) => record?.background ? ( <TextField source="background" record={record} className="pb-2" /> ) : null } /> // ...};This will display the “Referred By” information in the contact sidebar when available.
Deploying to Production
Section titled “Deploying to Production”It’s time to deploy your customized version of Atomic CRM to production. You use Supabase.com to host the backend, and GitHub Pages to host the frontend. Both services offer free plans that are sufficient for Atomic CRM.
First, login or register to Supabase.com.
Atomic CRM comes with a CLI utility to create a backend instance on Supabase.com:
make supabase-remote-initThe script will ask you for the Supabase instance name, create the database, apply the migrations and deploy the edge functions. Finally, it will create a .env.production.local file with your remote Supabase configuration.
The frontend of the CRM is a Single-Page App that can be deployed to any CDN. Since you have forked the Atomic CRM repository on GitHub, you can use GitHub Pages to host the frontend.
First, build the frontend bundle with:
npm run buildThis will create a dist directory with the built application made of static HTML, CSS, and JS files.
To deploy it to GitHub pages, use the following command:
npm run ghpages:deployAfter a couple minutes, your customized CRM will be available at https://<username>.github.io/atomic-crm/, and connected to the production Supabase instance you created earlier.
You can proceed with the creation of the first admin user and start using your CRM in production!
Next Steps
Section titled “Next Steps”Explore the documentation to learn more about Atomic CRM:
User Documentation
Section titled “User Documentation”Developer Documentation
Section titled “Developer Documentation”-
Customization
-
Deploying to Production