Architecture Choices
This document explains some of the architecture decisions made in the development of Atomic CRM.
Components
Section titled “Components”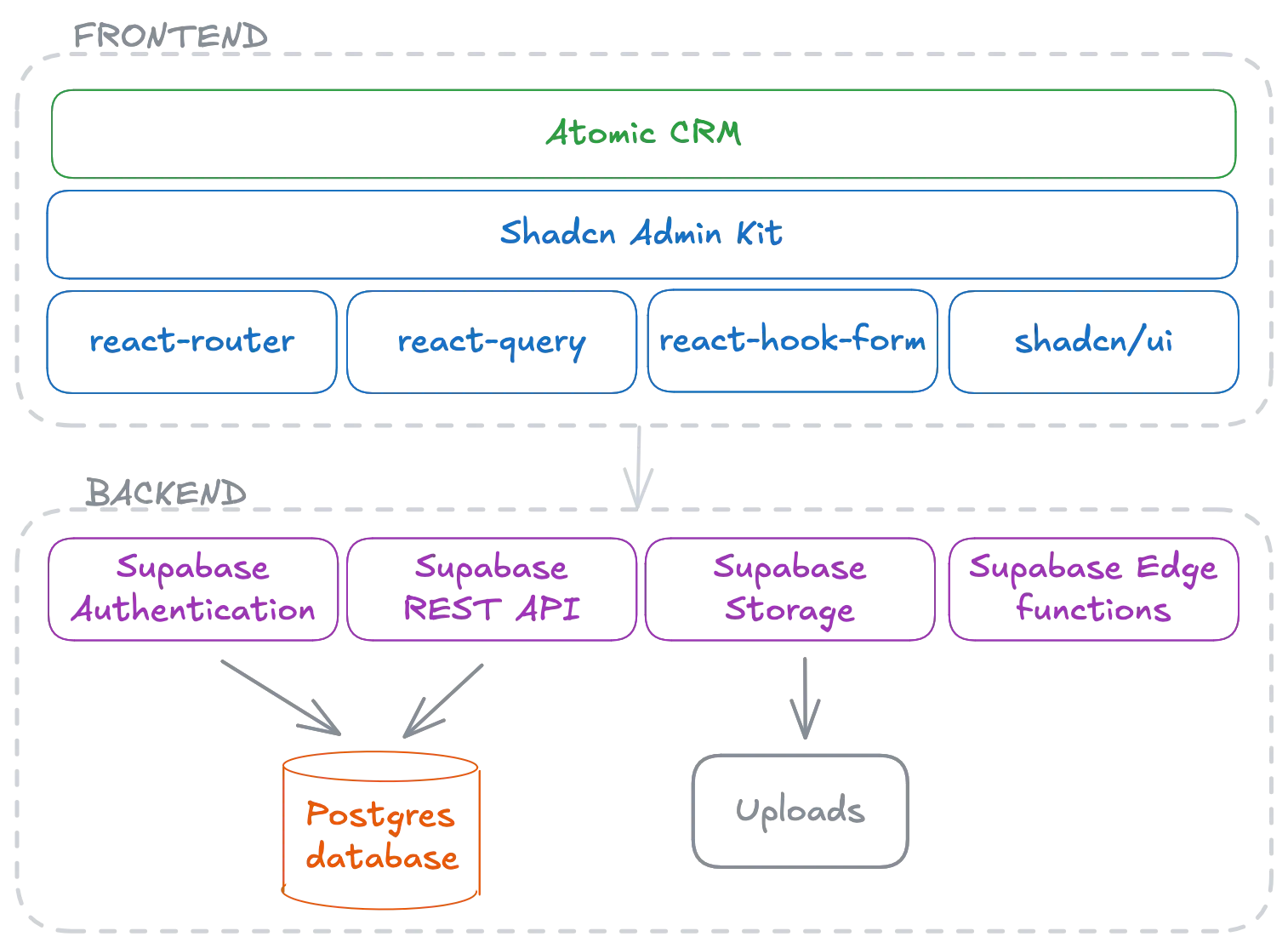
The frontend is a Single-Page Application built with Shadcn Admin Kit, a React application framework that glues together the most popular and robust React libraries, such as:
- React Router for routing
- React Query for data fetching and caching
- React Hook Form for form management
- Shadcn UI for beautiful, accessible, and customizable components
- Radix UI for accessible UI components
- Tailwind CSS for styling
For the backend, Atomic CRM leverages Supabase. Supabase provides a PostgreSQL database, a REST API, authentication, storage, and edge functions. In practice, this means that there is very little backend code to maintain (a few edge functions for user management and inbound email processing).
Mutable Dependencies
Section titled “Mutable Dependencies”The Atomic CRM code primarily lives in the src/components/atomic-crm directory. With less than 15,000 lines of code, it is a small codebase that can be easily customized.
The Atomic CRM code also contains some mutable dependencies, i.e. libraries that are directly integrated into the codebase to be modified if needed. These dependencies are located in the following directories:
src/components/admin: Shadcn Admin Kit, providing the frontend architecture and the glue code to integrate the various libraries.src/copmponents/ui: Shadcn UI, providing beautiful, accessible, and customizable components powered by Tailwind CSS.
You can modify or replaces the files in these directories. It’s the recommended way to customize the application.
If you want to upgrade these dependencies, you can follow the instructions in their respective documentation.
Some pages in Atomic CRM require data from multiple tables. To simplify the frontend code and reduce the HTTP overhead, Atomic CRM uses database views to abstract the complexity of the queries.
For instance, the contact list page displays the number of tasks for each contact. This information is provided by the contacts_summary view, defined in the supabase/migrations/init_db.sql file.
When using the FakeRest data provider, these views are emulated in the frontend.
Triggers
Section titled “Triggers”User credentials are stored in Supabase’s auth.users table. Supabase does not allow to add columns to this table. That’s why additional user details are stored in a sales table created by Atomic CRM. A database trigger is used to automatically sync the sales record when a user is created or updated (e.g. for the first_name and last_name fields).
The trigger can be found in the supabase/migrations/20240730075425_init_triggers.sql file.
Edge Functions
Section titled “Edge Functions”Due to the limitations of Supabase, the API does not have a public endpoint to manage users.
To solve this problem, Atomic CRM uses a users edge function in charge of:
- Verifying the current user’s permissions
- Creating and updating users
Atomic CRM does not support user deletion to avoid data losses. Yet, it is possible to disable a user’s account (relying on Supabase’s ban feature).
Atomic also uses Edge functions to handle the webhook and process the received emails. Check the Inbound Email documentation for more information.
The edge functions can be found in the supabase/functions/ directory.