<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>
This component allows adding or removing relationships between two resources sharing an associative table. The changes in the associative table are sent to the dataProvider when the user submits the form so that they can cancel the changes before submission.
Note: The <ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> cannot currently display multiple records with the same id from the end reference resource even though they might have different properties in the associative table.
This feature requires a valid is an Enterprise Edition subscription.
Let’s imagine that you’re writing an app managing concerts for artists. The data model features a many-to-many relationship between the bands and venues tables through a performances associative table.
┌─────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐│ bands │ │ performances │ │ venues ││---------│ │--------------│ │---------------││ id │───┐ │ id │ ┌──│ id ││ name │ └──╼│ band_id │ │ │ name ││ │ │ venue_id │╾──┘ │ location ││ │ │ date │ │ │└─────────┘ └──────────────┘ └───────────────┘In this example, bands.id matches performances.band_id, and performances.venue_id matches venues.id.
To let users edit the venues for given band in an <AutocompleteArrayInput>, wrap that input in a <ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> where you define the relationship via the reference, through and using props:
import { EditBase, Form } from 'ra-core';import { AutocompleteArrayInput, TextInput } from 'my-react-admin-ui-library';import { ReferenceManyToManyInputBase } from '@react-admin/ra-core-ee';
export const BandEdit = () => ( <EditBase mutationMode="optimistic"> <Form> <TextInput source="name" /> <ReferenceManyToManyInputBase reference="venues" through="performances" using="band_id,venue_id" > <AutocompleteArrayInput label="Performances" optionText="name" /> </ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> </Form> </EditBase>);<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> expects a child that is an input allowing to select multiple values as child - like <AutocompleteArrayInput> in the example above.
Note that although all possible child components support a defaultValue prop, it will only be applied on create views.
Tip: We don’t recommend using <ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> in an edition view that has its mutationMode set to undoable. Indeed, even if users cancel the main mutation, the changes in the associative table will still be applied.
Tip: If you need to edit the fields of the associative table (e.g. the date in performances), you can use a <ReferenceManyInputBase> instead of <ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>.
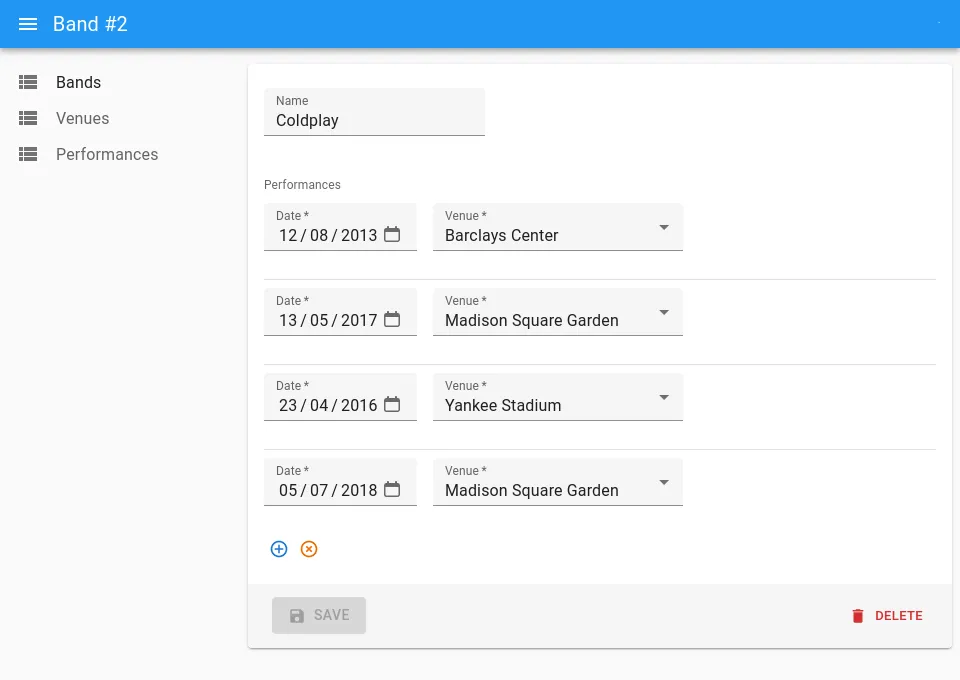
You will need to let users select the related record (venue in the example above) via a <ReferenceInputBase>:
import { EditBase, Form, ReferenceInputBase, required } from 'ra-core';import { AutocompleteArrayInput, DateInput, SelectInput, SimpleFormIterator, TextInput,} from 'my-react-admin-ui-library';import { ReferenceManyInputBase } from '@react-admin/ra-core-ee';
const BandEdit = () => ( <Edit mutationMode="optimistic"> <Form> <TextInput source="name" /> <ReferenceManyInputBase reference="performances" target="band_id"> <SimpleFormIterator inline disableReordering> <DateInput source="date" /> <ReferenceInputBase reference="venues" source="venue_id"> <SelectInput optionText="name" /> </ReferenceInputBase> </SimpleFormIterator> </ReferenceManyInputBase> </Form> </Edit>);Limitation: <ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> cannot be used to filter a list.
| Prop | Required | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
children | Required | element | - | A select array input element (e.g. <SelectArrayInput>). |
reference | Required | string | - | Name of the reference resource, e.g. ‘venues’ |
through | Required | string | - | Name of the resource for the associative table, e.g. ‘book_authors’ |
filter | Optional | object | {} | Filter for the associative table (passed to the getManyReference() call) |
filter Choices | Optional | object | {} | Filter for the possible choices fetched from the reference table (passed to the getList() call) |
mutationOptions | Optional | { meta, onError } | - | Mutation options for the create and deleteMany calls. Only meta and onError are supported. |
perPage | Optional | number | 25 | Limit for the number of results fetched from the associative table |
perPage Choices | Optional | number | 25 | Limit for the number of possible choices fetched from the reference table |
queryOptions | Optional | UseQueryOptions | - | Query options for the getList, getMany and getManyReference calls |
sort | Optional | { field: string, order: 'ASC' or 'DESC' } | { field: 'id', order: 'DESC' } | Sort for the associative table (passed to the getManyReference() call) |
sort Choices | Optional | { field: string, order: 'ASC' or 'DESC' } | { field: 'id', order: 'DESC' } | Sort for the possible choices fetched from the reference table (passed to the getList() call) |
source | Optional | string | 'id' | Name of the field containing the identity of the main resource. Used determine the value to look for in the associative table. |
using | Optional | string | '([resource]_id,[reference]_id)' | Tuple (comma separated) of the two field names used as foreign keys, e.g ‘book_id,author_id’. The tuple should start with the field pointing to the resource, and finish with the field pointing to the reference |
children
Section titled “children”<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> expects an select component as child, i.e. a component working inside a ChoiceContext.
import { EditBase, Form, ReferenceInputBase, required } from 'ra-core';import { SelectArrayInput, DateInput, SelectInput, SimpleFormIterator, TextInput,} from 'my-react-admin-ui-library';import { ReferenceManyToManyInputBase } from '@react-admin/ra-core-ee';
const BandEdit = () => ( <Edit mutationMode="optimistic"> <Form> <TextInput source="name" /> <ReferenceManyToManyInputBase reference="venues" through="performances" using="band_id,venue_id" filter={{ date: '2018-08-31' }} > <SelectArrayInput /> </ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> </Form> </Edit>);filter
Section titled “filter”You can filter the records of the associative table (e.g. performances) using the filter prop. This filter is passed to the getManyReference() call.
<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase reference="venues" through="performances" using="band_id,venue_id" filter={{ date: '2018-08-31' }}> {/* ... */}</ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>filterChoices
Section titled “filterChoices”<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> displays a list of possible values from the reference table (e.g. venues) as suggestions in the input. It uses the getList() dataProvider call to fetch these possible values.
You can filter the possible values of the reference table using the filterChoices prop. This filterChoices is passed to the getList() call.
<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase reference="venues" through="performances" using="band_id,venue_id" filterChoice={{ location: 'New York' }}> {/* ... */}</ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>mutationOptions
Section titled “mutationOptions”Use the mutationOptions prop to customize the create and deleteMany mutations.
You can for instance use it to pass a custom meta to the dataProvider.
<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase reference="venues" through="performances" using="band_id,venue_id" mutationOptions={{ meta: { myParameter: 'value' } }}> {/* ... */}</ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>You can also use it to pass an onError function as follows:
<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase reference="venues" through="performances" using="band_id,venue_id" mutationOptions={{ onError: (error, step, data) => console.warn({ error, step, data }) }}> {/* ... */}</ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>perPage
Section titled “perPage”By default, <ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> displays at most 25 entries from the associative table (e.g. 25 performances). You can change the limit by setting the perPage prop:
<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase reference="venues" through="performances" using="band_id,venue_id" perPage={10}> {/* ... */}</ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>perPageChoices
Section titled “perPageChoices”<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> displays a list of possible values from the reference table (e.g. venues) as suggestions in the input. It uses the getList() dataProvider call to fetch these possible values.
By default, react-admin displays at most 25 possible values from the reference table (e.g. 25 venues). You can change the limit by setting the perPageChoices prop:
<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase reference="venues" through="performances" using="band_id,venue_id" perPageChoices={10}> {/* ... */}</ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>queryOptions
Section titled “queryOptions”Use the queryOptions prop to customize the queries for getList, getMany and getManyReference.
You can for instance use it to pass a custom meta to the dataProvider.
<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase reference="venues" through="performances" using="band_id,venue_id" queryOptions={{ meta: { myParameter: 'value' } }}> {/* ... */}</ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>reference
Section titled “reference”The name of the target resource to fetch.
For instance, if you want to display the venues of a given bands, through performances, the reference name should be venues:
<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase source="id" reference="venues" resource="bands" through="performances"> {/* ... */}</ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>By default, <ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> orders the possible values by id desc for the associative table (e.g. performances). You can change this order by setting the sort prop (an object with field and order properties) to be applied to the associative resource.
<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase reference="venues" through="performances" using="band_id,venue_id" sort={{ field: 'id', order: 'DESC' }}> {/* ... */}</ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>sortChoices
Section titled “sortChoices”By default, <ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> orders the possible values by id desc for the reference table (e.g. venues). You can change this order by setting the sortChoices prop (an object with field and order properties).
<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase reference="venues" through="performances" using="band_id,venue_id" sortChoices={{ field: 'id', order: 'DESC' }}> {/* ... */}</ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>source
Section titled “source”By default, <ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> uses the id field as target for the reference. If the foreign key points to another field of your record, you can select it with the source prop:
<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase source="_id" reference="venues" resource="bands" through="performances"> {/* ... */}</ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>through
Section titled “through”You must specify the associative table name using the through prop.
<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase reference="venues" through="performances"> {/* ... */}</ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>You can specify the columns to use in the associative using the using prop.
<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase reference="venues" through="performances" using="band_id,venue_id"> {/* ... */}</ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>Limitations
Section titled “Limitations”<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>cannot be used inside an<ArrayInputBase>, a<ReferenceOneInputBase>or a<ReferenceManyInputBase>.<ReferenceManyToManyInputBase>does not support server side validation.
dataProvider Calls
Section titled “dataProvider Calls”When rendered, <ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> fetches the dataProvider three times in a row:
- once to get the records of the associative resource (
performancesin this case), using agetManyReference()call - once to get the records of the reference resource (
venuesin this case), using agetMany()call. - once to get the possible values of the reference resource (
venuesin this case) to show as suggestions in the input, using agetList()call
For instance, if the user edits the band of id 123, <ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> first issues the following query to the dataProvider:
dataProvider.getManyReference('venues', { target: 'band_id', id: 123,});Let’s say that the dataProvider returns the following response:
{ "data": [ { "id": 667, "band_id": 123, "venue_id": 732 }, { "id": 895, "band_id": 123, "venue_id": 874 } { "id": 901, "band_id": 123, "venue_id": 756 } ], "total": 3}Then, <ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> issues a second query to the dataProvider:
dataProvider.getMany('venues', { ids: [732, 874, 756],});Which returns the following:
{ "data": [ { "id": 732, "name": "Madison Square Garden" }, { "id": 874, "name": "Yankee Stadium" } { "id": 874, "name": "Barclays Center" } ]}That’s enough to display the current value in the input. But to display venues suggestions, the component makes a final call:
dataProvider.getList('venues', { sort: { field: 'id', order: 'DESC' }, pagination: { page: 1, perPage: 25 }, filter: {},});{ "data": [ { "id": 732, "name": "Madison Square Garden" }, { "id": 874, "name": "Yankee Stadium" } { "id": 874, "name": "Barclays Center" } ... ], "total": 32}And that’s it for the display phase.
When the user submits the form, the save function compares the value of the <ReferenceManyToManyInputBase> (the list of relationships edited by the user) with the value previously returned by the dataProvider. Using a diffing algorithm, it deduces a list of insertions and deletions in the associative table, that are executed all at once.
For instance, let’s say that after displaying the venues 732 and 874 where bands 123 performs, the user removes venue 732, and adds venues 2 and 3. Upon submission, the dataProvider will detect removals and additions, and send the following queries:
dataProvider.delete('performances', { id: 667, previousData: { id: 667, band_id: 123, venue_id: 732 },});dataProvider.create('performances', { data: { band_id: 123, venue_id: 2 },});dataProvider.create('performances', { data: { band_id: 123, venue_id: 3 },});This component uses specific translations for displaying notifications. As for all translations in react-admin, it’s possible to customize the messages.
To create your own translations, you can use the TypeScript types to see the structure and see which keys are overridable.
Here is an example of how to customize translations in your app:
import polyglotI18nProvider from 'ra-i18n-polyglot';import englishMessages from 'ra-language-english';import frenchMessages from 'ra-language-french';import { raRelationshipsLanguageEnglish, raRelationshipsLanguageFrench, type RaRelationshipsTranslationMessages,} from '@react-admin/ra-core-ee';import { CoreAdmin, mergeTranslations, type TranslationMessages as BaseTranslationMessages } from 'ra-core';
/* TranslationMessages extends the default translation * Type from ra-core (BaseTranslationMessages) * and the ra-Relationships translation Type (RaRelationshipsTranslationMessages) */interface TranslationMessages extends RaRelationshipsTranslationMessages, BaseTranslationMessages {}
const customEnglishMessages: TranslationMessages = mergeTranslations( englishMessages, raRelationshipsLanguageEnglish, { 'ra-relationships': { referenceManyToManyInput: { saveError: 'Server error: your changes were not completely saved', }, }, });
const i18nCustomProvider = polyglotI18nProvider(locale => { if (locale === 'fr') { return mergeTranslations(frenchMessages, raRealTimeLanguageFrench); } return customEnglishMessages;}, 'en');
export const MyApp = () => ( <CoreAdmin i18nProvider={i18nCustomProvider}> ... </CoreAdmin>);