<ReferenceManyToManyField>
This Enterprise Edition
<SingleFieldList>).
Note: The <ReferenceManyToManyField> cannot currently display multiple records with the same id from the end reference resource, even though they might have different properties in the associative table.
Usage
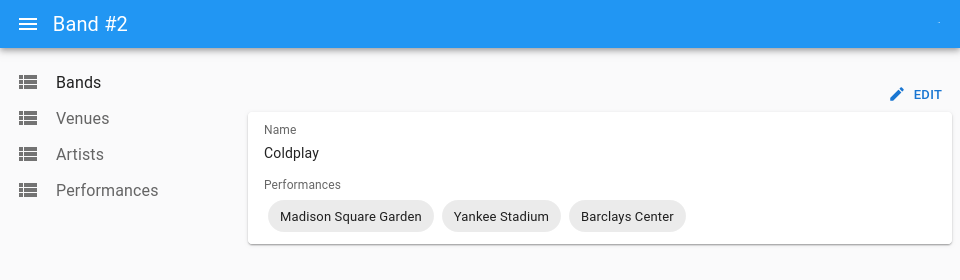
Let’s imagine that you’re writing an app managing concerts for artists. The data model features a many-to-many relationship between the bands and venues tables through a performances associative table.
┌─────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐
│ bands │ │ performances │ │ venues │
│---------│ │--------------│ │---------------│
│ id │───┐ │ id │ ┌──│ id │
│ name │ └──╼│ band_id │ │ │ name │
│ │ │ venue_id │╾──┘ │ location │
│ │ │ date │ │ │
└─────────┘ └──────────────┘ └───────────────┘
In this example, bands.id matches performances.band_id, and performances.venue_id matches venues.id.
To allow users see the venues for a given band in <SingleFieldList>, wrap that component in <ReferenceManyToManyField> where you define the relationship via the reference, through and using props:
import React from 'react';
import { Show, SimpleShowLayout, TextField, DateField, SingleFieldList, ChipField } from 'react-admin';
import { ReferenceManyToManyField } from '@react-admin/ra-relationships';
export const BandShow = () => (
<Show>
<SimpleShowLayout>
<TextField source="name" />
<ReferenceManyToManyField
reference="venues"
through="performances"
using="band_id,venue_id"
label="Performances"
>
<SingleFieldList>
<ChipField source="name" />
</SingleFieldList>
</ReferenceManyToManyField>
<EditButton />
</SimpleShowLayout>
</Show>
);
Props
| Prop | Required | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
children |
Required | element |
- | An iterator element (e.g. <SingleFieldList> or <Datagrid>). The iterator element usually has one or more child <Field> components. |
reference |
Required | string |
- | Name of the reference resource, e.g. ‘venues’ |
through |
Required | string |
- | Name of the resource for the associative table, e.g. ‘performances’ |
filter |
Optional | object |
{} |
Filter for the associative table (passed to the getManyReference() call) |
joinLimit |
Optional | number |
100 | Limit for the number of results fetched from the associative table. Should be greater than perPage |
perPage |
Optional | number |
25 | Limit the number of displayed result after getManyReference is called. Useful when using a pagination component. Should be smaller than joinLimit |
sort |
Optional | { field: string, order: 'ASC' or 'DESC' } |
{ field: 'id', order: 'DESC' } |
Sort for the associative table (passed to the getManyReference() call) |
source |
Optional | string |
'id' |
Name of the field containing the identity of the main resource. Used determine the value to look for in the associative table. |
using |
Optional | string |
'[resource]_id,[reference]_id' |
Tuple (comma separated) of the two field names used as foreign keys, e.g ‘band_id,venue_id’. The tuple should start with the field pointing to the resource, and finish with the field pointing to the reference |
children
<ReferenceManyToManyField> expects an iterator component as child, i.e. a component working inside a ListContext.
This means you can use a <Datagrid> instead of a <SingleFieldList>, which is useful if you want to display more details about related records. For instance, to display the venue name and location:
export const BandShow = () => (
<Show>
<SimpleShowLayout>
<TextField source="name" />
<ReferenceManyToManyField
reference="venues"
through="performances"
using="band_id,venue_id"
label="Performances"
>
- <SingleFieldList>
- <ChipField source="name" />
- </SingleFieldList>
+ <Datagrid>
+ <TextField source="name" />
+ <TextField source="location" />
+ </Datagrid>
</ReferenceManyToManyField>
<EditButton />
</SimpleShowLayout>
</Show>
);
filter
You can filter the records of the associative table (e.g. performances) using the filter prop. This filter is passed to the getManyReference() call.
<ReferenceManyToManyField
reference="venues"
through="performances"
using="band_id,venue_id"
filter={{ date: '2018-08-31' }}
>
{/* ... */}
</ReferenceManyToManyField>
joinLimit
By default, react-admin fetches 100 entries in the join table (e.g. performances). You can decrease or increase the number of entries fetched from the associative table by modifying the joinLimit prop:
import { Pagination } from 'react-admin';
<ReferenceManyToManyField
reference="venues"
through="performances"
using="band_id,venue_id"
joinLimit={50}
>
{/* ... */}
</ReferenceManyToManyField>
perPage
By default, react-admin displays at most 25 entries from the associative table (e.g. 25 performances). You can change the limit by setting the perPage prop:
<ReferenceManyToManyField
reference="venues"
through="performances"
using="band_id,venue_id"
perPage={10}
>
{/* ... */}
</ReferenceManyToManyField>
Note: You can add a pagination system by adding the <Pagination> component to the <ReferenceManyToManyField> children:
import { Pagination } from 'react-admin';
<ReferenceManyToManyField
reference="venues"
through="performances"
using="band_id,venue_id"
perPage={10}
>
{/* ... */}
<Pagination />
</ReferenceManyToManyField>
reference
The name of the target resource to fetch.
For instance, if you want to display the venues of a given bands, through performances, the reference name should be venues:
<ReferenceManyToManyField
source="id"
reference="venues"
resource="bands"
through="performances"
>
{/* ... */}
</ReferenceManyToManyField>
sort
By default, react-admin orders the possible values by id desc for the associative table (e.g. performances). You can change this order by setting the sort prop (an object with field and order properties) to be applied to the associative resource.
<ReferenceManyToManyField
reference="venues"
through="performances"
using="band_id,venue_id"
sort={{ field: 'id', order: 'DESC' }}
>
{/* ... */}
</ReferenceManyToManyField>
source
By default, <ReferenceManyToManyField> uses the id field as target for the reference. If the foreign key points to another field of your record, you can select it with the source prop
<ReferenceManyToManyField
source="_id"
reference="venues"
resource="bands"
through="performances"
>
{/* ... */}
</ReferenceManyToManyField>
through
You must specify the associative table name using the through prop.
<ReferenceManyToManyField reference="venues" through="performances">
{/* ... */}
</ReferenceManyToManyField>
using
You can specify the columns to use in the associative using the using prop.
<ReferenceManyToManyField
reference="venues"
through="performances"
using="band_id,venue_id"
>
{/* ... */}
</ReferenceManyToManyField>
DataProvider Calls
<ReferenceManyToManyField> fetches the dataProvider twice in a row:
- once to get the records of the associative resource (
performancesin this case), using agetManyReference()call - once to get the records of the reference resource (
venuesin this case), using agetMany()call.
For instance, if the user displays the band of id 123, <ReferenceManyToManyField> first issues the following query to the dataProvider:
dataProvider.getManyReference('performances', {
target: 'band_id',
id: 123,
});
Let’s say that the dataProvider returns the following response:
{
"data": [
{ "id": 667, "band_id": 123, "venue_id": 732 },
{ "id": 895, "band_id": 123, "venue_id": 874 }
{ "id": 901, "band_id": 123, "venue_id": 756 }
],
"total": 3
}
Then, <ReferenceManyToManyField> issues a second query to the dataProvider:
dataProvider.getMany('venues', {
ids: [732, 874, 756],
});
And receives the reference venues:
{
"data": [
{ "id": 732, "name": "Madison Square Garden" },
{ "id": 874, "name": "Yankee Stadium" }
{ "id": 874, "name": "Barclays Center" }
],
"total": 3
}
