<ReferenceField>
<ReferenceField> is useful for displaying many-to-one and one-to-one relationships, e.g. the details of a user when rendering a post authored by that user.
Usage
For instance, let’s consider a model where a post has one author from the users resource, referenced by a user_id field.
┌──────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐
│ posts │ │ users │
│--------------│ │----------------│
│ id │ ┌───│ id │
│ user_id │╾──┘ │ name │
│ title │ │ date_of_birth │
│ published_at │ └────────────────┘
└──────────────┘
In that case, use <ReferenceField> to display the post author’s as follows:
import { Show, SimpleShowLayout, ReferenceField, TextField, DateField } from 'react-admin';
export const PostShow = () => (
<Show>
<SimpleShowLayout>
<TextField source="id" />
<TextField source="title" />
<DateField source="published_at" />
<ReferenceField source="user_id" reference="users" label="Author" />
</SimpleShowLayout>
</Show>
);
<ReferenceField> fetches the data, puts it in a RecordContext, and renders the recordRepresentation (the record id field by default) wrapped in a link to the related user <Edit> page.
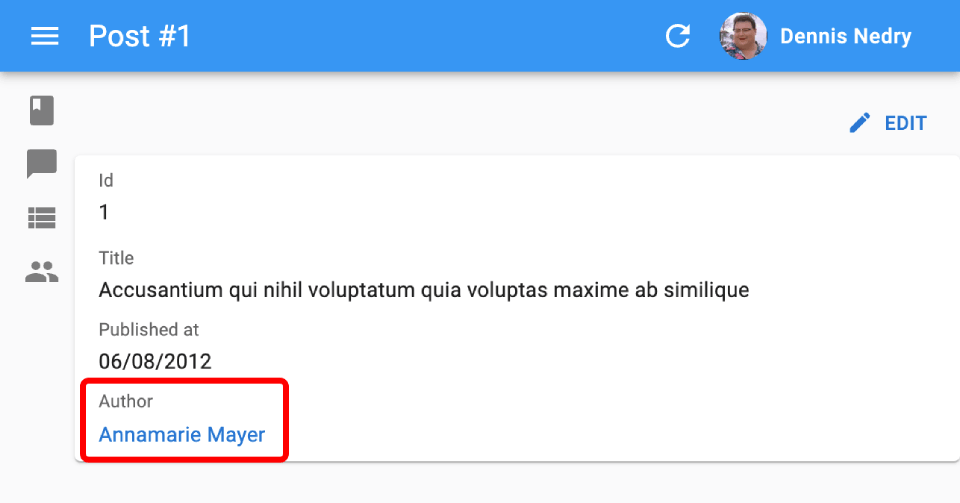
So it’s a good idea to configure the <Resource recordRepresentation> to render related records in a meaningul way. For instance, for the users resource, if you want the <ReferenceField> to display the full name of the author:
<Resource
name="users"
list={UserList}
recordRepresentation={(record) => `${record.first_name} ${record.last_name}`}
/>
Alternately, if you pass a child component, <ReferenceField> will render it instead of the recordRepresentation. Usual child components for <ReferenceField> are other <Field> components (e.g. <TextField>).
<ReferenceField source="user_id" reference="users">
<TextField source="name" />
</ReferenceField>
This component fetches a referenced record (users in this example) using the dataProvider.getMany() method, and passes it to its child.
It uses dataProvider.getMany() instead of dataProvider.getOne() for performance reasons. When using several <ReferenceField> in the same page (e.g. in a <Datagrid>), this allows to call the dataProvider once instead of once per row.
Props
| Prop | Required | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
source |
Required | string |
- | Name of the property to display |
reference |
Required | string |
- | The name of the resource for the referenced records, e.g. ‘posts’ |
children |
Optional | ReactNode |
- | One or more Field elements used to render the referenced record |
emptyText |
Optional | string |
’’ | Defines a text to be shown when the field has no value or when the reference is missing |
label |
Optional | string | Function |
resources. [resource]. fields.[source] |
Label to use for the field when rendered in layout components |
link |
Optional | string | Function |
edit |
Target of the link wrapping the rendered child. Set to false to disable the link. |
queryOptions |
Optional | UseQuery Options |
{} |
react-query client options |
sortBy |
Optional | string | Function |
source |
Name of the field to use for sorting when used in a Datagrid |
<ReferenceField> also accepts the common field props.
emptyText
<ReferenceField> can display a custom message when the referenced record is missing, thanks to the emptyText prop.
<ReferenceField source="user_id" reference="users" emptyText="Missing user" />
<ReferenceField> renders the emptyText:
- when the referenced record is missing (no record in the
userstable with the rightuser_id), or - when the field is empty (no
user_idin the record).
label
By default, <SimpleShowLayout>, <Datagrid> and other layout components infer the label of a field based on its source. For a <ReferenceField>, this may not be what you expect:
{/* default label is 'User Id', or the translation of 'resources.posts.fields.user_id' if it exists */}
<ReferenceField source="user_id" reference="users" />
That’s why you often need to set an explicit label on a <ReferenceField>:
<ReferenceField label="Author name" source="user_id" reference="users" />
React-admin uses the i18n system to translate the label, so you can use translation keys to have one label for each language supported by the interface:
<ReferenceField label="resources.posts.fields.author" source="user_id" reference="users" />
link
To change the link from the <Edit> page to the <Show> page, set the link prop to “show”.
<ReferenceField source="user_id" reference="users" link="show" />
You can also prevent <ReferenceField> from adding a link to children by setting link to false.
// No link
<ReferenceField source="user_id" reference="users" link={false} />
You can also use a custom link function to get a custom path for the children. This function must accept record and reference as arguments.
// Custom path
<ReferenceField
source="user_id"
reference="users"
link={(record, reference) => `/my/path/to/${reference}/${record.id}`}
/>
queryOptions
Use the queryOptions prop to pass options to the dataProvider.getMany() query that fetches the referenced record.
For instance, to pass a custom meta:
<ReferenceField
source="user_id"
reference="users"
queryOptions={{ meta: { foo: 'bar' } }}
>
<TextField source="name" />
</ReferenceField>
reference
The resource to fetch for the related record.
For instance, if the posts resource has a user_id field, set the reference to users to fetch the user related to each post.
<ReferenceField source="user_id" reference="users" />
sortBy
By default, when used in a <Datagrid>, and when the user clicks on the column header of a <ReferenceField>, react-admin sorts the list by the field source. To specify another field name to sort by, set the sortBy prop.
<ReferenceField source="user_id" reference="users" sortBy="user.name" />
sx: CSS API
The <ReferenceField> component accepts the usual className prop. You can also override many styles of the inner components thanks to the sx property (see the sx documentation for syntax and examples). This property accepts the following subclasses:
| Rule name | Description |
|---|---|
& .RaReferenceField-link |
Applied to each child element |
To override the style of all instances of <ReferenceField> using the application-wide style overrides, use the RaReferenceField key.
Performance
When used in a <Datagrid>, <ReferenceField> fetches the referenced record only once for the entire table.
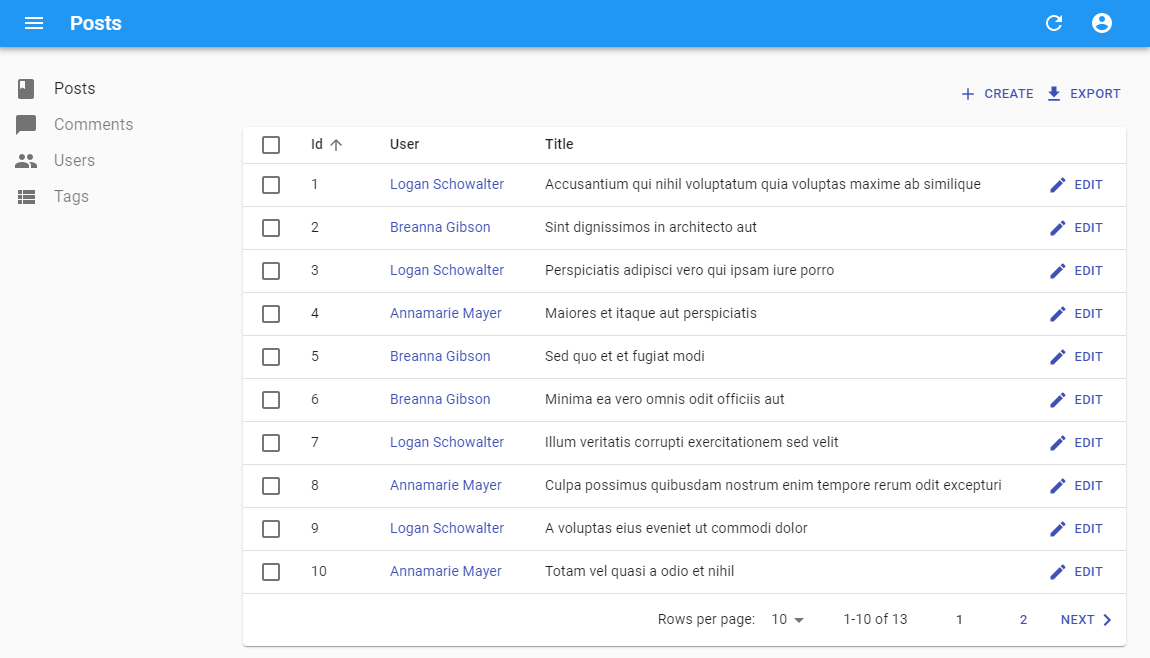
For instance, with this code:
import { List, Datagrid, ReferenceField, TextField, EditButton } from 'react-admin';
export const PostList = () => (
<List>
<Datagrid>
<TextField source="id" />
<ReferenceField label="User" source="user_id" reference="users" />
<TextField source="title" />
<EditButton />
</Datagrid>
</List>
);
React-admin accumulates and deduplicates the ids of the referenced records to make one dataProvider.getMany() call for the entire list, instead of n dataProvider.getOne() calls. So for instance, if the API returns the following list of posts:
[
{
id: 123,
title: 'Totally agree',
user_id: 789,
},
{
id: 124,
title: 'You are right my friend',
user_id: 789
},
{
id: 125,
title: 'Not sure about this one',
user_id: 735
}
]
Then react-admin renders the <PostList> with a loader for the <ReferenceField>, fetches the API for the related users in one call (dataProvider.getMany('users', { ids: [789,735] }), and re-renders the list once the data arrives. This accelerates the rendering and minimizes network load.
Prefetching
When you know that a page will contain a <ReferenceField>, you can configure the main page query to prefetch the referenced records to avoid a flicker when the data arrives. To do so, pass a meta.prefetch parameter to the page query.
For example, the following code prefetches the authors referenced by the posts:
const PostList = () => (
<List queryOptions={{ meta: { prefetch: ['author'] } }}>
<Datagrid>
<TextField source="title" />
{/** renders without an additional request */}
<ReferenceField source="author_id" />
</Datagrid>
</List>
);
Note: For prefetching to function correctly, your data provider must support Prefetching Relationships. Refer to your data provider’s documentation to verify if this feature is supported.
Note: Prefetching is a frontend performance feature, designed to avoid flickers and repaints. It doesn’t always prevent <ReferenceField> to fetch the data. For instance, when coming to a show view from a list view, the main record is already in the cache, so the page renders immediately, and both the page controller and the <ReferenceField> controller fetch the data in parallel. The prefetched data from the page controller arrives after the first render of the <ReferenceField>, so the data provider fetches the related data anyway. But from a user perspective, the page displays immediately, including the <ReferenceField>. If you want to avoid the <ReferenceField> to fetch the data, you can use the React Query Client’s staleTime option.
Rendering More Than One Field
You often need to render more than one field of the reference table (e.g. if the users table has a first_name and a last_name field).
Given that <ReferenceField> can accept more than one child, you can use as many <Field> as you like:
import { Show, SimpleShowLayout, ReferenceField, TextField, DateField, FunctionField } from 'react-admin';
export const PostShow = () => (
<Show>
<SimpleShowLayout>
<TextField source="id" />
<TextField source="title" />
<DateField source="published_at" />
<ReferenceField label="Author" source="user_id" reference="users">
<TextField source="first_name" />{' '}
<TextField source="last_name" />
</ReferenceField>
</SimpleShowLayout>
</Show>
);
You can also use several <ReferenceField> for the same resource in a given view - react-admin will deduplicate them and only make one call to the distant table. This is useful e.g. is you want to have one label per field:
import { Show, SimpleShowLayout, ReferenceField, TextField, DateField } from 'react-admin';
export const PostShow = () => (
<Show>
<SimpleShowLayout>
<TextField source="id" />
<TextField source="title" />
<DateField source="published_at" />
<ReferenceField label="First name" source="user_id" reference="users">
<TextField source="first_name" />
</ReferenceField>
<ReferenceField label="Last name" source="user_id" reference="users">
<TextField source="last_name" />
</ReferenceField>
</SimpleShowLayout>
</Show>
);
You can also use a <FunctionField> to render a string composed of several fields.
import { Show, SimpleShowLayout, ReferenceField, TextField, DateField, FunctionField } from 'react-admin';
export const PostShow = () => (
<Show>
<SimpleShowLayout>
<TextField source="id" />
<TextField source="title" />
<DateField source="published_at" />
<ReferenceField label="Name" source="user_id" reference="users">
<FunctionField render={record => `${record.first_name} ${record.last_name}`} />
</ReferenceField>
</SimpleShowLayout>
</Show>
);
Removing The Link
You can prevent <ReferenceField> from adding a link to its children by setting link to false.
// No link
<ReferenceField source="user_id" reference="users" link={false} />
Access Control
If your authProvider implements the canAccess method and you don’t provide the link prop, React-Admin will verify whether users have access to the Show and Edit views.
For instance, given the following ReferenceField:
<ReferenceField source="user_id" reference="users" />
React-Admin will call canAccess with the following parameters:
- If the
usersresource has a Show view:{ action: "show", resource: 'posts', record: Object } - If the
usersresource has an Edit view:{ action: "edit", resource: 'posts', record: Object }

