<Layout>
The default react-admin layout renders a horizontal app bar at the top, a navigation menu on the side, and the main content in the center.
In addition, the layout renders the menu as a dropdown on mobile.
React-admin lets you override the app layout using the <Admin layout> prop. You can use any component you want as layout ; but if you just need to tweak the default layout, you can use the <Layout> component.
Usage
Create a custom layout overriding some of the props of the default layout. Remember to pass down the children prop:
// in src/MyLayout.js
import { Layout } from 'react-admin';
import { MyAppBar } from './MyAppBar';
export const MyLayout = ({ children }) => (
<Layout appBar={MyAppBar}>
{children}
</Layout>
);
Then pass this custom layout to the <Admin> component:
Instead of the default layout, you can use your own component as the admin layout. Just use the layout prop of the <Admin> component:
// in src/App.js
import { MyLayout } from './MyLayout';
const App = () => (
<Admin layout={MyLayout} dataProvider={...}>
// ...
</Admin>
);
Props
| Prop | Required | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
children |
Required | Element |
- | The content of the layout |
appBar |
Optional | Component |
- | A React component rendered at the top of the layout |
appBarAlwaysOn |
Optional | boolean |
- | When true, the app bar is always visible |
className |
Optional | string |
- | Passed to the root <div> component |
error |
Optional | Component |
- | A React component rendered in the content area in case of error |
menu |
Optional | Component |
- | A React component rendered at the side of the screen |
sidebar |
Optional | Component |
- | A React component responsible for rendering the menu (e.g. in a drawer) |
sx |
Optional | SxProps |
- | Style overrides, powered by MUI System |
appBar
Lets you override the top App Bar.
// in src/MyLayout.js
import * as React from 'react';
import { Layout } from 'react-admin';
import { MyAppBar } from './MyAppBar';
export const MyLayout = ({ children }) => (
<Layout appBar={MyAppBar}>
{children}
</Layout>
);
You can use react-admin’s <AppBar> component as a base for your custom app bar, or the component of your choice.
By default, react-admin’s <AppBar> displays the page title. You can override this default by passing children to <AppBar> - they will replace the default title. And if you still want to include the page title defined by each page, make sure you include the <TitlePortal> element (which uses React Portals).
Here is a custom app bar component extending <AppBar> to include a company logo in the center of the page header:
// in src/MyAppBar.js
import * as React from 'react';
import { AppBar, TitlePortal } from 'react-admin';
import Box from '@mui/material/Box';
import Logo from './Logo';
export const MyAppBar = () => (
<AppBar color="primary">
<TitlePortal />
<Box flex="1" />
<Logo />
<Box flex="1" />
</AppBar>
);
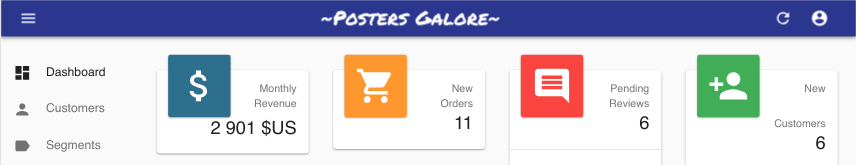
Check out the <AppBar> documentation for more information, and for instructions on building your own AppBar.
appBarAlwaysOn
By default, the app bar is hidden when the user scrolls down the page. This is useful to save space on small screens. But if you want to keep the app bar always visible, you can set the appBarAlwaysOn prop to true.
// in src/MyLayout.js
import * as React from 'react';
import { Layout } from 'react-admin';
export const MyLayout = ({ children }) => (
<Layout appBarAlwaysOn>
{children}
</Layout>
);
className
className is passed to the root <div> component. It lets you style the layout with CSS - but the sx prop is preferred.
error
React-admin uses React’s Error Boundaries to render a user-friendly error page in case of client-side JavaScript error, using an internal component called <Error>. In production mode, it only displays a generic error message. In development mode, this error page contains the error message and stack trace.
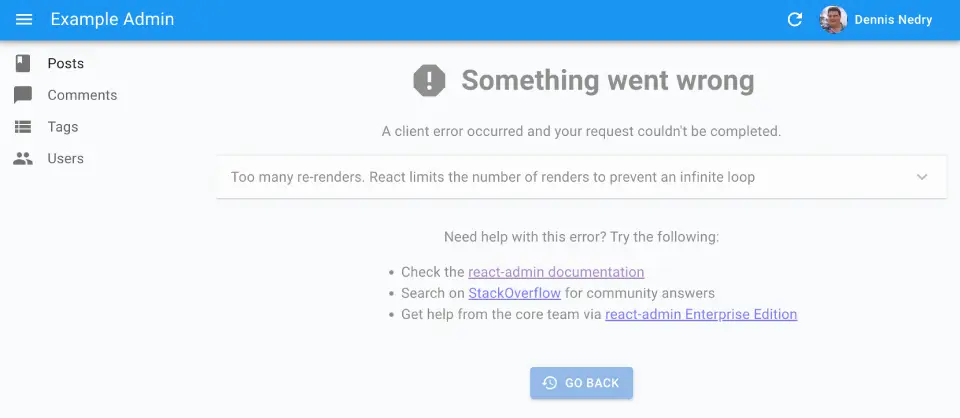
If you want to customize this error page (e.g. to log the error in a monitoring service), create your own error component, and pass it to a custom Layout, as follows:
// in src/MyLayout.js
import { Layout } from 'react-admin';
import { MyError } from './MyError';
export const MyLayout = ({ children }) => (
<Layout error={MyError}>
{children}
</Layout>
);
React-admin relies on the react-error-boundary package for handling error boundaries. So your custom error component will receive the error, the error info, and a resetErrorBoundary function as props. You should call resetErrorBoundary upon navigation to remove the error screen.
Here is an example of a custom error component:
// in src/MyError.js
import Button from '@mui/material/Button';
import ErrorIcon from '@mui/icons-material/Report';
import History from '@mui/icons-material/History';
import { Title, useTranslate, useDefaultTitle, useResetErrorBoundaryOnLocationChange } from 'react-admin';
export const MyError = ({
error,
resetErrorBoundary,
...rest
}) => {
useResetErrorBoundaryOnLocationChange(resetErrorBoundary);
const translate = useTranslate();
const defaultTitle = useDefaultTitle();
return (
<div>
<Title title={`${defaultTitle}: Error`} />
<h1><ErrorIcon /> Something Went Wrong </h1>
<div>A client error occurred and your request couldn't be completed.</div>
{process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && (
<details>
<h2>{translate(error.message)}</h2>
{errorInfo.componentStack}
</details>
)}
<div>
<Button
variant="contained"
startIcon={<History />}
onClick={() => history.go(-1)}
>
Back
</Button>
</div>
</div>
);
};
Tip: React-admin uses the default <Error> component as error boundary twice: once in <Layout> for error happening in CRUD views, and once in <Admin> for errors happening in the layout. If you want to customize the error page in the entire app, you should also pass your custom error component to the <Admin error> prop. See the Admin error prop documentation for more details.
menu
Lets you override the menu.
// in src/Layout.js
import { Layout } from 'react-admin';
import { MyMenu } from './MyMenu';
export const Layout = ({ children }) => (
<Layout menu={MyMenu}>
{children}
</Layout>
);
You can create a custom menu component using react-admin’s <Menu> component:
// in src/MyMenu.js
import * as React from 'react';
import { Menu } from 'react-admin';
import BookIcon from '@mui/icons-material/Book';
import ChatBubbleIcon from '@mui/icons-material/ChatBubble';
import PeopleIcon from '@mui/icons-material/People';
import LabelIcon from '@mui/icons-material/Label';
export const MyMenu = () => (
<Menu>
<Menu.DashboardItem />
<Menu.Item to="/posts" primaryText="Posts" leftIcon={<BookIcon />}/>
<Menu.Item to="/comments" primaryText="Comments" leftIcon={<ChatBubbleIcon />}/>
<Menu.Item to="/users" primaryText="Users" leftIcon={<PeopleIcon />}/>
<Menu.Item to="/custom-route" primaryText="Miscellaneous" leftIcon={<LabelIcon />}/>
</Menu>
);
The <Layout menu> component can render any component you like - not just a component based on <Menu>.
React-admin provides alternative menu layouts that you can use as a base for your own menu:
<MultiLevelMenu>to render nested menus<IconMenu>for a narrow icon bar with dropdown menus
And you can build a totally custom menu using Material UI’s <Menu> component.
sidebar
You can override the default sidebar using this prop. The default sidebar will display a permanent drawer when the window size is above Material UI theme’s sm breakpoint, and a temporary drawer when the window size is less than that.
If you wish to always display a temporary drawer, you can customize using the following sample code:
// in src/Layout.js
import * as React from 'react';
import { Layout } from 'react-admin';
import { MySidebar } from './MySidebar';
export const Layout = ({ children }) => (
<Layout sidebar={MySidebar}>
{children}
</Layout>
);
// in src/MySidebar.js
import * as React from 'react';
import { Drawer } from '@mui/material';
import { SidebarClasses, useLocale, useSidebarState } from 'react-admin';
export const MySidebar = ({ children }) => {
const [open, setOpen] = useSidebarState();
useLocale(); // force redraw on locale change
const toggleSidebar = () => setOpen(!open);
return (
<Drawer
variant="temporary"
open={open}
onClose={toggleSidebar}
classes={SidebarClasses}
>
{children}
</Drawer>
);
};
You can specify the Sidebar width by setting the width and closedWidth properties on a custom Material UI theme:
import { defaultTheme } from 'react-admin';
const theme = {
...defaultTheme,
sidebar: {
width: 300, // The default value is 240
closedWidth: 70, // The default value is 55
},
};
const App = () => (
<Admin theme={theme} dataProvider={...}>
// ...
</Admin>
);
For more advanced sidebar theming, create a new Sidebar component overiding the default one with the sx prop:
import { Sidebar, Layout } from 'react-admin';
const MySidebar = (props) => (
<Sidebar
sx={{
"& .RaSidebar-drawerPaper": {
backgroundColor: "red",
},
}}
{...props}
/>
);
const MyLayout = ({ children }) => (
<Layout sidebar={MySidebar}>
{children}
</Layout>
);
sx: CSS API
Pass an sx prop to customize the style of the main component and the underlying elements.
export const MyLayout = ({ children }) => (
<Layout sx={{ '& .RaLayout-appFrame': { marginTop: 55 } }}>
{children}
</Layout>
);
This property accepts the following subclasses:
| Rule name | Description |
|---|---|
& .RaLayout-appFrame |
Applied to the application frame containing the appBar, the sidebar, and the main content |
& .RaLayout-contentWithSidebar |
Applied to the main part containing the sidebar and the content |
& .RaLayout-content |
Applied to the content area |
To override the style of <Layout> using the application-wide style overrides, use the RaLayout key.
Tip: If you need to override global styles (like the default font size or family), you should write a custom theme rather than override the <Layout sx> prop. And if you need to tweak the default layout to add a right column or move the menu to the top, you’re probably better off writing your own layout component.
Adding A Custom Context
A custom Layout is the ideal place to add an application-wide context.
For instance, in a multi-tenant application, you may want to add a tenant context to your layout.
// in src/MyLayout.js
import { Layout } from 'react-admin';
import { TenantContext } from './TenantContext';
const getCookie = (name) => document.cookie
.split('; ')
.find(row => row.startsWith(`${name}=`))
?.split('=')[1];
export const MyLayout = ({ children }) => (
<TenantContext.Provider value={getCookie('tenant')}>
<Layout>
{children}
</Layout>
</TenantContext.Provider>
);
Adding Developer Tools
A custom layout is also the ideal place to add debug tools, e.g. react-query devtools:
// in src/MyLayout.js
import { Layout } from 'react-admin';
import { ReactQueryDevtools } from '@tanstack/react-query-devtools'
export const MyLayout = ({ children }) => (
<Layout>
{children}
<ReactQueryDevtools />
</Layout>
);
Alternative Layouts
If you can’t configure <Layout> to render the layout you want, you can use an alternative layout component:
<ContainerLayout>is centered layout with horizontal navigation.<SolarLayout>is a layout with a small icon sidebar, no top bar, and a full-width content area.
You can also write your own layout component from scratch (see below).
Writing A Layout From Scratch
For more custom layouts, write a component from scratch. Your custom layout will receive the page content as children, so it should render it somewhere.
In its simplest form, a custom layout is just a component that renders its children:
const MyLayout = ({ children }) => (
<div>
<h1>My App</h1>
<main>{children}</main>
</div>
);
You can use the default layout as a starting point for your custom layout. Here is a simplified version (with no responsive support):
// in src/MyLayout.js
import { Box } from '@mui/material';
import { AppBar, Menu, Sidebar } from 'react-admin';
const MyLayout = ({ children }) => (
<Box
display="flex"
flexDirection="column"
zIndex={1}
minHeight="100vh"
backgroundColor="theme.palette.background.default"
position="relative"
>
<Box
display="flex"
flexDirection="column"
overflowX="auto"
>
<AppBar />
<Box display="flex" flexGrow={1}>
<Sidebar>
<Menu />
</Sidebar>
<Box
display="flex"
flexDirection="column"
flexGrow={2}
p={3}
marginTop="4em"
paddingLeft={5}
>
{children}
</Box>
</Box>
</Box>
</Box>
);
export default MyLayout;

