<List>
The <List> component is the root component for list pages. It fetches a list of records from the data provider, puts it in a ListContext, renders the default list page layout (title, buttons, filters, pagination), and renders its children. Usual children of <List>, like <Datagrid>, are responsible for displaying the list of records.
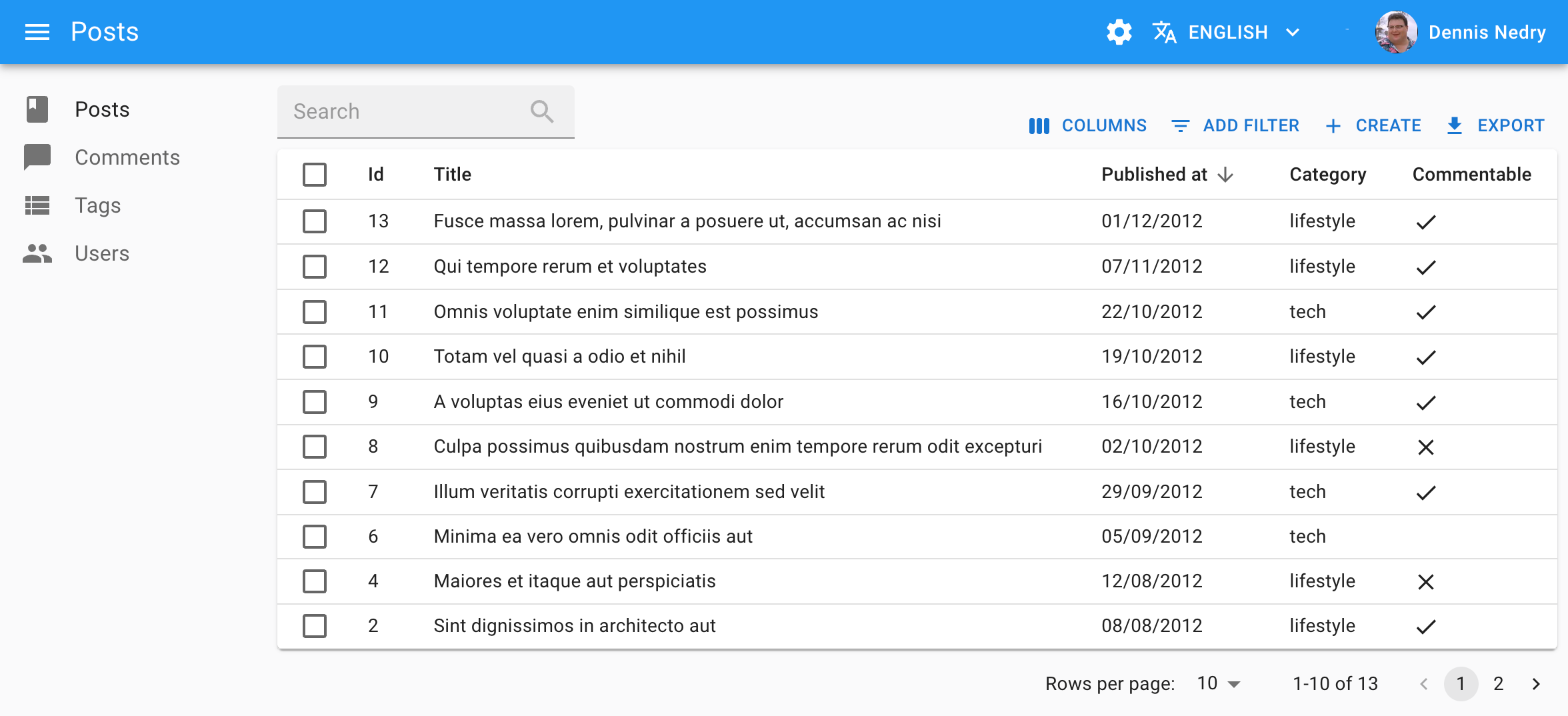
Usage
Here is the minimal code necessary to display a list of posts using a <Datagrid>:
// in src/posts.jsx
import { List, Datagrid, TextField, DateField, BooleanField } from 'react-admin';
export const PostList = () => (
<List>
<Datagrid>
<TextField source="id" />
<TextField source="title" />
<DateField source="published_at" />
<TextField source="category" />
<BooleanField source="commentable" />
</Datagrid>
</List>
);
// in src/App.jsx
import { Admin, Resource } from 'react-admin';
import jsonServerProvider from 'ra-data-json-server';
import { PostList } from './posts';
const App = () => (
<Admin dataProvider={jsonServerProvider('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com')}>
<Resource name="posts" list={PostList} />
</Admin>
);
export default App;
That’s enough to display a basic post list, with functional sort and pagination.
You can find more advanced examples of <List> usage in the demos.
Props
| Prop | Required | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
children |
Required | ReactNode |
- | The component to use to render the list of records. |
actions |
Optional | ReactElement |
- | The actions to display in the toolbar. |
aside |
Optional | ReactElement |
- | The component to display on the side of the list. |
component |
Optional | Component |
Card |
The component to render as the root element. |
debounce |
Optional | number |
500 |
The debounce delay in milliseconds to apply when users change the sort or filter parameters. |
disable Authentication |
Optional | boolean |
false |
Set to true to disable the authentication check. |
disable SyncWithLocation |
Optional | boolean |
false |
Set to true to disable the synchronization of the list parameters with the URL. |
empty |
Optional | ReactElement |
- | The component to display when the list is empty. |
emptyWhileLoading |
Optional | boolean |
false |
Set to true to return null while the list is loading. |
exporter |
Optional | function |
- | The function to call to export the list. |
filters |
Optional | ReactElement |
- | The filters to display in the toolbar. |
filter |
Optional | object |
- | The permanent filter values. |
filterDefaultValues |
Optional | object |
- | The default filter values. |
hasCreate |
Optional | boolean |
false |
Set to true to show the create button. |
pagination |
Optional | ReactElement |
<Pagination> |
The pagination component to use. |
perPage |
Optional | number |
10 |
The number of records to fetch per page. |
queryOptions |
Optional | object |
- | The options to pass to the useQuery hook. |
resource |
Optional | string |
- | The resource name, e.g. posts. |
sort |
Optional | object |
- | The initial sort parameters. |
storeKey |
Optional | string |
- | The key to use to store the current filter & sort. |
title |
Optional | string |
- | The title to display in the App Bar. |
sx |
Optional | object |
- | The CSS styles to apply to the component. |
Additional props are passed down to the root component (a MUI <Card> by default).
actions
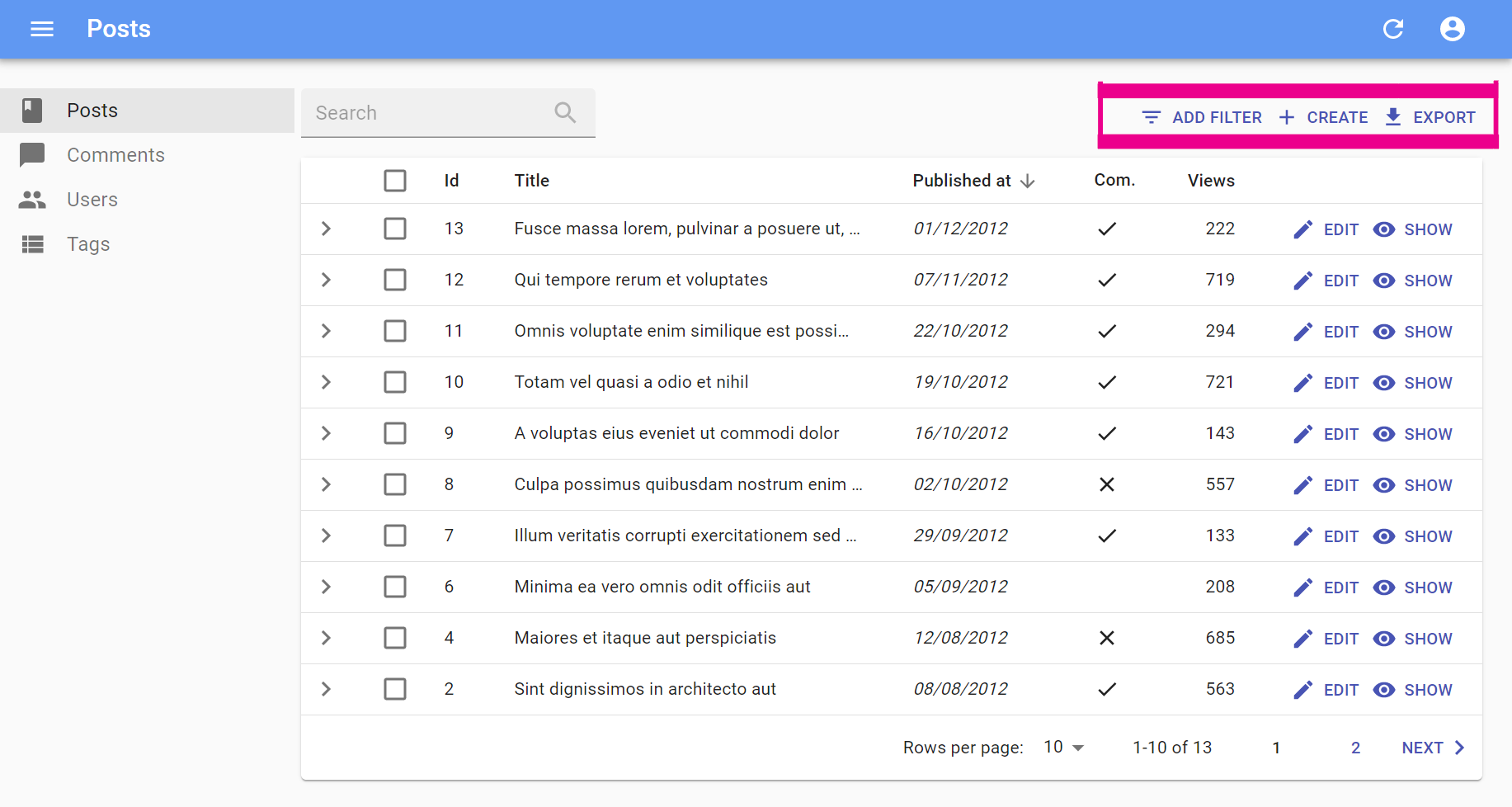
You can replace the list of default actions by your own elements using the actions prop:
import {
TopToolbar,
FilterButton,
CreateButton,
ExportButton,
Button,
List
} from 'react-admin';
import IconEvent from '@mui/icons-material/Event';
const ListActions = () => (
<TopToolbar>
<FilterButton/>
<CreateButton/>
<ExportButton/>
{/* Add your custom actions */}
<Button
onClick={() => { alert('Your custom action'); }}
label="Show calendar"
>
<IconEvent/>
</Button>
</TopToolbar>
);
export const PostList = () => (
<List actions={<ListActions/>}>
...
</List>
);
Use the useListContext hook to customize the actions depending on the list context, and the usePermissions to show/hide buttons depending on permissions. For example, you can hide the <CreateButton> when the user doesn’t have the right permission, and disable the <ExportButton> when the list is empty:
import {
useListContext,
usePermissions,
TopToolbar,
FilterButton,
CreateButton,
ExportButton,
List
} from 'react-admin';
import IconEvent from '@mui/icons-material/Event';
const ListActions = () => {
const { total, isLoading } = useListContext();
const { permissions } = usePermissions();
return (
<TopToolbar>
<FilterButton />
{permissions === "admin" && <CreateButton/>}
<ExportButton disabled={isLoading || total === 0} />
</TopToolbar>
);
}
aside: Side Component
You may want to display additional information on the side of the list. Use the aside prop for that, passing the component of your choice:
const Aside = () => (
<div style={{ width: 200, margin: '1em' }}>
<Typography variant="h6">Post details</Typography>
<Typography variant="body2">
Posts will only be published once an editor approves them
</Typography>
</div>
);
const PostList = () => (
<List aside={<Aside />}>
...
</List>
);
The aside component can call the useListContext() hook to receive the same props as the <List> child component. This means you can display additional details of the current list in the aside component:
import { Typography } from '@mui/material';
import { useListContext } from 'react-admin';
const Aside = () => {
const { data, isLoading } = useListContext();
if (isLoading) return null;
return (
<div style={{ width: 200, margin: '1em' }}>
<Typography variant="h6">Posts stats</Typography>
<Typography variant="body2">
Total views: {data.reduce((sum, post) => sum + post.views, 0)}
</Typography>
</div>
);
};
The aside prop is also the preferred way to add a Filter Sidebar to a list view:
// in src/PostFilterSidebar.js
import { SavedQueriesList, FilterLiveSearch, FilterList, FilterListItem } from 'react-admin';
import { Card, CardContent } from '@mui/material';
import MailIcon from '@mui/icons-material/MailOutline';
import CategoryIcon from '@mui/icons-material/LocalOffer';
export const PostFilterSidebar = () => (
<Card sx={{ order: -1, mr: 2, mt: 9, width: 200 }}>
<CardContent>
<SavedQueriesList />
<FilterLiveSearch >
<FilterList label="Subscribed to newsletter" icon={<MailIcon />}>
<FilterListItem label="Yes" value={{ has_newsletter: true }} />
<FilterListItem label="No" value={{ has_newsletter: false }} />
</FilterList>
<FilterList label="Category" icon={<CategoryIcon />}>
<FilterListItem label="Tests" value={{ category: 'tests' }} />
<FilterListItem label="News" value={{ category: 'news' }} />
<FilterListItem label="Deals" value={{ category: 'deals' }} />
<FilterListItem label="Tutorials" value={{ category: 'tutorials' }} />
</FilterList>
</CardContent>
</Card>
);
// in src/PostList.js
import { PostFilterSidebar } from './PostFilterSidebar';
export const PostList = () => (
<List aside={<PostFilterSidebar />}>
...
</List>
);
Tip: the <Card sx> prop in the PostFilterSidebar component above is here to put the sidebar on the left side of the screen, instead of the default right side.
children: List Layout
<List> itself doesn’t render the list of records. It delegates this task to its children components. These children components grab the data from the ListContext and render them on screen.
The most common List child is <Datagrid>:
export const BookList = () => (
<List>
<Datagrid>
<TextField source="id" />
<TextField source="title" />
<TextField source="author" />
<TextField source="year" />
</Datagrid>
</List>
);
React-admin provides several components that can read and display a list of records from a ListContext, each with a different layout:
<Datagrid>displays records in a table<EditableDatagrid>displays records in a table AND lets users edit them inline<SimpleList>displays records in a list without many details - suitable for mobile devices<Tree>displays records in a tree structure<Calendar>displays event records in a calendar<SingleFieldList>displays records inline, showing one field per record
So for instance, you can use a <SimpleList> instead of a <Datagrid> to display a list of books on a mobile device:
export const BookList = () => (
<List>
- <Datagrid>
- <TextField source="id" />
- <TextField source="title" />
- <TextField source="author" />
- <TextField source="year" />
- </Datagrid>
+ <SimpleList
+ primaryText={record => <i>record.title</i>}
+ secondaryText={record => <>By {record.author} ({record.year})</>}
+ />
+ </List>
);
You can also render the list of records in a custom way. You’ll need to grab the data from the ListContext using <WithListContext>:
import { List, WithListContext } from 'react-admin';
import { Stack, Typography } from '@mui/material';
const BookList = () => (
<List>
<WithListContext render={({ data }) => (
<Stack spacing={2} sx={{ padding: 2 }}>
{data?.map(book => (
<Typography key={book.id}>
<i>{book.title}</i>, by {book.author} ({book.year})
</Typography>
))}
</Stack>
)} />
</List>
);
Check Building a custom List Iterator for more details.
component
By default, the List view renders the main content area inside a Material UI <Card> element. The actual layout of the list depends on the child component you’re using (<Datagrid>, <SimpleList>, or a custom layout component).
Some List layouts display each record in a <Card>, in which case the user ends up seeing a card inside a card, which is bad UI. To avoid that, you can override the main area container by passing a component prop:
// use a div as root component
const PostList = () => (
<List component="div">
...
</List>
);
// use a custom component as root component
const PostList = () => (
<List component={MyComponent}>
...
</List>
);
The default value for the component prop is Card.
debounce
By default, <List> does not refresh the data as soon as the user enters data in the filter form. Instead, it waits for half a second of user inactivity (via lodash.debounce) before calling the dataProvider on filter change. This is to prevent repeated (and useless) calls to the API.
You can customize the debounce duration in milliseconds - or disable it completely - by passing a debounce prop to the <List> component:
// wait 1 seconds instead of 500 milliseconds befoce calling the dataProvider
const PostList = () => (
<List debounce={1000}>
...
</List>
);
disableAuthentication
By default, all pages using <List> require the user to be authenticated - any anonymous access redirects the user to the login page.
If you want to allow anonymous access to a List page, set the disableAuthentication prop to true.
import { List } from 'react-admin';
const BoolkList = () => (
<List disableAuthentication>
...
</List>
);
disableSyncWithLocation
By default, react-admin synchronizes the <List> parameters (sort, pagination, filters) with the query string in the URL (using react-router location) and the Store.
When you use a <List> component anywhere else than as <Resource list>, you may want to disable this synchronization to keep the parameters in a local state, independent for each <List> instance. This allows to have multiple lists on a single page. The drawback is that a hit on the “back” button doesn’t restore the previous list parameters. To do so, pass the disableSyncWithLocation prop.
const Dashboard = () => (
<div>
// ...
<ResourceContextProvider value="posts">
<List disableSyncWithLocation>
<SimpleList
primaryText={record => record.title}
secondaryText={record => `${record.views} views`}
tertiaryText={record => new Date(record.published_at).toLocaleDateString()}
/>
</List>
</ResourceContextProvider>
<ResourceContextProvider value="comments">
<List disableSyncWithLocation>
<SimpleList
primaryText={record => record.title}
secondaryText={record => `${record.views} views`}
tertiaryText={record => new Date(record.published_at).toLocaleDateString()}
/>
</List>
</ResourceContextProvider>
</div>
)
Tip: As disableSyncWithLocation also disables the persistence of the list parameters in the Store, the storeKey prop is ignored when disableSyncWithLocation is set to true.
Please note that the selection state is not synced in the URL but in a global store using the resource as key. Thus, all lists in the page using the same resource will share the same selection state. This is a design choice because if row selection is not tied to a resource, then when a user deletes a record it may remain selected without any ability to unselect it. If you want the selection state to be local, you will have to implement your own useListController hook and pass a custom key to the useRecordSelection hook. You will then need to implement your own DeleteButton and BulkDeleteButton to manually unselect rows when deleting records.
empty: Empty Page Component
When there is no result, and there is no active filter, and the resource has a create page, react-admin displays a special page inviting the user to create the first record.
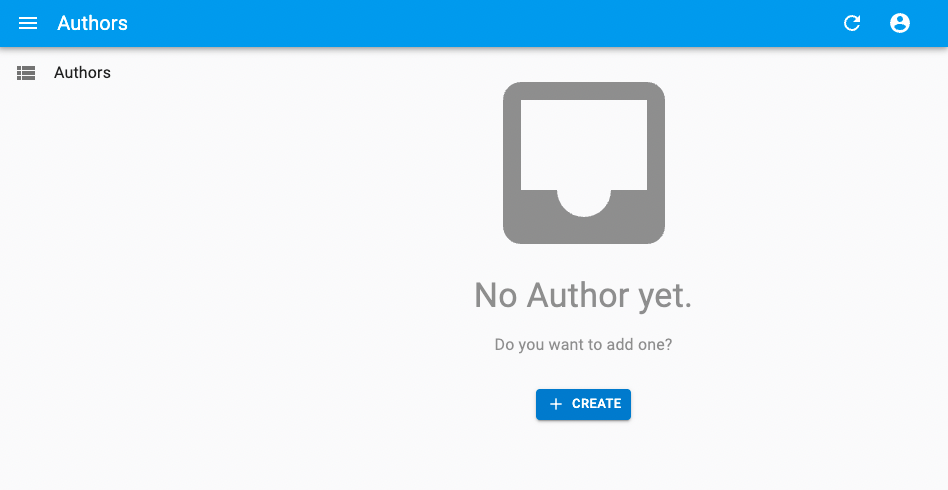
You can use the empty prop to replace that page by a custom component:
import { Box, Button, Typography } from '@mui/material';
import { CreateButton, List } from 'react-admin';
const Empty = () => (
<Box textAlign="center" m={1}>
<Typography variant="h4" paragraph>
No products available
</Typography>
<Typography variant="body1">
Create one or import from a file
</Typography>
<CreateButton />
<Button onClick={/* ... */}>Import</Button>
</Box>
);
const ProductList = () => (
<List empty={<Empty />}>
...
</List>
);
The empty component can call the useListContext() hook to receive the same props as the List child component.
You can also set the empty props value to false to bypass the empty page display and render an empty list instead.
import { List } from 'react-admin';
const ProductList = () => (
<List empty={false}>
...
</List>
);
emptyWhileLoading
Default layout components (<Datagrid> and <SimpleList>) return null when the data is loading. If you use a custom layout component instead, you’ll have to handle the case where the data is not yet defined.
That means that the following will fail on load with a “ReferenceError: data is not defined” error:
import { List, useListContext } from 'react-admin';
import { Stack, Typography } from '@mui/icons-material/Star';
const SimpleBookList = () => {
const { data } = useListContext();
return (
<Stack spacing={2}>
{data.map(book => (
<Typography key={book.id}>
<i>{book.title}</i>, by {book.author} ({book.year})
</Typography>
))}
</Stack>
);
}
const BookList = () => (
<List>
<SimpleBookList />
</List>
);
You can handle this case by getting the isLoading variable from the useListContext hook:
const SimpleBookList = () => {
const { data, isLoading } = useListContext();
if (isLoading) return null;
return (
<Stack spacing={2}>
{data.map(book => (
<Typography key={book.id}>
<i>{book.title}</i>, by {book.author} ({book.year})
</Typography>
))}
</Stack>
);
}
The <List emptyWhileLoading> prop provides a convenient shortcut for that use case. When enabled, <List> won’t render its child until data is defined.
const BookList = () => (
- <List>
+ <List emptyWhileLoading>
<SimpleBookList />
</List>
);
exporter
Among the default list actions, react-admin includes an <ExportButton>. This button is disabled when there is no record in the current <List>.
By default, clicking this button will:
- Call the
dataProviderwith the current sort and filter (but without pagination), - Transform the result into a CSV string,
- Download the CSV file.
The columns of the CSV file match all the fields of the records in the dataProvider response. That means that the export doesn’t take into account the selection and ordering of fields in your <List> via Field components. If you want to customize the result, pass a custom exporter function to the <List>. This function will receive the data from the dataProvider (after step 1) and replace steps 2-3 (i.e. it’s in charge of transforming, converting, and downloading the file).
Tip: For CSV conversion, you can import jsonexport, a CSV to JSON converter which is already a react-admin dependency. And for CSV download, take advantage of react-admin’s downloadCSV function.
Here is an example for a Posts exporter, omitting, adding, and reordering fields:
// in PostList.js
import { List, downloadCSV } from 'react-admin';
import jsonExport from 'jsonexport/dist';
const exporter = posts => {
const postsForExport = posts.map(post => {
const { backlinks, author, ...postForExport } = post; // omit backlinks and author
postForExport.author_name = post.author.name; // add a field
return postForExport;
});
jsonExport(postsForExport, {
headers: ['id', 'title', 'author_name', 'body'] // order fields in the export
}, (err, csv) => {
downloadCSV(csv, 'posts'); // download as 'posts.csv` file
});
};
const PostList = () => (
<List exporter={exporter}>
...
</List>
)
In many cases, you’ll need more than simple object manipulation. You’ll need to augment your objects based on relationships. For instance, the export for comments should include the title of the related post - but the export only exposes a post_id by default. For that purpose, the exporter receives a fetchRelatedRecords function as the second parameter. It fetches related records using your dataProvider.getMany() method and returns a promise.
Here is an example for a Comments exporter, fetching related Posts:
// in CommentList.js
import { List, downloadCSV } from 'react-admin';
import jsonExport from 'jsonexport/dist';
const exporter = (records, fetchRelatedRecords) => {
// will call dataProvider.getMany('posts', { ids: records.map(record => record.post_id) }), ignoring duplicate and empty post_id
fetchRelatedRecords(records, 'post_id', 'posts').then(posts => {
const data = records.map(record => ({
...record,
post_title: posts[record.post_id].title,
}));
return jsonExport(data, {
headers: ['id', 'post_id', 'post_title', 'body'],
}, (err, csv) => {
downloadCSV(csv, 'comments');
});
});
};
const CommentList = () => (
<List exporter={exporter}>
...
</List>
)
Tip: If you need to call another verb in the exporter, take advantage of the third parameter passed to the function: it’s the dataProvider function.
Tip: The <ExportButton> limits the main request to the dataProvider to 1,000 records. If you want to increase or decrease this limit, pass a maxResults prop to the <ExportButton> in a custom <ListActions> component.
Tip: React-admin also provides a <BulkExportButton> component that depends on the exporter, and that you can use in the bulkActionButtons prop of the <List> component.
Tip: For complex (or large) exports, fetching all the related records and assembling them client-side can be slow. In that case, create the CSV on the server side, and replace the <ExportButton> component by a custom one, fetching the CSV route.
Tip: You may also remove the <ExportButton> by passing false to the exporter prop: exporter={false}
Tip: Looking for an <ImportButton>? React-admin doesn’t provide this feature, but the community has an excellent third-party module for CSV import: benwinding/react-admin-import-csv.
filters: Filter Inputs
You can add an array of filter Inputs to the List using the filters prop:
const postFilters = [
<TextInput label="Search" source="q" alwaysOn />,
<TextInput label="Title" source="title" defaultValue="Hello, World!" />,
];
export const PostList = () => (
<List filters={postFilters}>
...
</List>
);
Tip: Don’t mix up this filters prop, expecting an array of <Input> elements, with the filter props, which expects an object to define permanent filters (see below).
Tip: Filters will render as disabled inputs or menu items (depending on filter context) if passed the prop disabled.
Filter Inputs are regular inputs. <List> hides them all by default, except those that have the alwaysOn prop.
You can also display filters as a sidebar:
For more details about customizing filters, see the Filtering the List section.
filter: Permanent Filter
You can choose to always filter the list, without letting the user disable this filter - for instance to display only published posts. Write the filter to be passed to the data provider in the filter props:
// in src/posts.js
export const PostList = () => (
<List filter={{ is_published: true }}>
...
</List>
);
The actual filter parameter sent to the data provider is the result of the combination of the user filters (the ones set through the filters component form), and the permanent filter. The user cannot override the permanent filters set by way of filter.
filterDefaultValues
To set default values to filters, you can either pass an object literal as the filterDefaultValues prop of the <List> element, or use the defaultValue prop of any input component.
There is one exception: inputs with alwaysOn don’t accept defaultValue. You have to use the filterDefaultValues for those.
// in src/posts.js
const postFilters = [
<TextInput label="Search" source="q" alwaysOn />,
<BooleanInput source="is_published" alwaysOn />,
<TextInput source="title" defaultValue="Hello, World!" />,
];
export const PostList = () => (
<List filters={postFilters} filterDefaultValues={{ is_published: true }}>
...
</List>
);
Tip: The filter and filterDefaultValues props have one key difference: the filterDefaultValues can be overridden by the user, while the filter values are always sent to the data provider. Or, to put it otherwise:
const filterSentToDataProvider = { ...filterDefaultValues, ...filterChosenByUser, ...filter };
hasCreate
The List page shows a Create button if the resource has a create view, or if the hasCreate prop is set to true. Using this prop lets you force the display of the create button, or hide it.
export const PostList = () => (
<List hasCreate={false}>
...
</List>
);
pagination: Pagination Component
The pagination prop allows to replace the default pagination controls by your own.
// in src/MyPagination.js
import { Pagination, List } from 'react-admin';
const PostPagination = props => <Pagination rowsPerPageOptions={[10, 25, 50, 100]} {...props} />;
export const PostList = () => (
<List pagination={<PostPagination />}>
...
</List>
);
See Paginating the List for details.
perPage: Pagination Size
By default, the list paginates results by groups of 10. You can override this setting by specifying the perPage prop:
// in src/posts.js
export const PostList = () => (
<List perPage={25}>
...
</List>
);
Note: The default pagination component’s rowsPerPageOptions includes options of 5, 10, 25 and 50. If you set your List perPage to a value not in that set, you must also customize the pagination so that it allows this value, or else there will be an error.
// in src/MyPagination.js
-import { List } from 'react-admin';
+import { List, Pagination } from 'react-admin';
export const PostList = () => (
- <List perPage={6}>
+ <List perPage={6} pagination={<Pagination rowsPerPageOptions={[6, 12, 24, 36]} />}>
...
</List>
);
queryOptions
<List> accepts a queryOptions prop to pass options to the react-query client.
This can be useful e.g. to pass a custom meta to the dataProvider.getList() call.
import { List } from 'react-admin';
const PostList = () => (
<List queryOptions={{ meta: { foo: 'bar' } }}>
...
</List>
);
With this option, react-admin will call dataProvider.getList() on mount with the ` meta: { foo: ‘bar’ }` option.
You can also use the queryOptions prop to override the default error side effect. By default, when the dataProvider.getList() call fails, react-admin shows an error notification.
You can override this behavior and pass custom side effects by providing a queryOptions prop:
import { useNotify, useRedirect, List } from 'react-admin';
const PostList = () => {
const notify = useNotify();
const redirect = useRedirect();
const onError = (error) => {
notify(`Could not load list: ${error.message}`, { type: 'error' });
redirect('/dashboard');
};
return (
<List queryOptions={{ onError }}>
...
</List>
);
}
The onError function receives the error from the dataProvider call (dataProvider.getList()), which is a JavaScript Error object (see the dataProvider documentation for details).
resource
By default, <List> operates on the current ResourceContext (defined at the routing level), so under the /posts path, the resource prop will be posts. You may want to force a different resource for a list. In this case, pass a custom resource prop, and it will override the ResourceContext value.
export const UsersList = () => (
<List resource="users">
...
</List>
);
sort: Default Sort Field & Order
Pass an object literal as the sort prop to determine the default field and order used for sorting:
export const PostList = () => (
<List sort={{ field: 'published_at', order: 'DESC' }}>
...
</List>
);
sort defines the default sort order ; the list remains sortable by clicking on column headers.
For more details on list sort, see the Sorting The List section below.
storeKey
To display multiple lists of the same resource and keep distinct store states for each of them (filters, sorting and pagination), specify unique keys with the storeKey property.
In case no storeKey is provided, the states will be stored with the following key: ${resource}.listParams.
Note: Please note that selection state will remain linked to a resource-based key as described here.
In the example below, both lists NewerBooks and OlderBooks use the same resource (‘books’), but their controller states are stored separately (under the store keys 'newerBooks' and 'olderBooks' respectively). This allows to use both components in the same app, each having its own state (filters, sorting and pagination).
import {
Admin,
CustomRoutes,
Resource,
List,
Datagrid,
TextField,
} from 'react-admin';
import { Route } from 'react-router-dom';
const NewerBooks = () => (
<List
resource="books"
storeKey="newerBooks"
sort={{ field: 'year', order: 'DESC' }}
>
<Datagrid>
<TextField source="id" />
<TextField source="title" />
<TextField source="author" />
<TextField source="year" />
</Datagrid>
</List>
);
const OlderBooks = () => (
<List
resource="books"
storeKey="olderBooks"
sort={{ field: 'year', order: 'ASC' }}
>
<Datagrid>
<TextField source="id" />
<TextField source="title" />
<TextField source="author" />
<TextField source="year" />
</Datagrid>
</List>
);
const Admin = () => {
return (
<Admin dataProvider={dataProvider}>
<CustomRoutes>
<Route path="/newerBooks" element={<NewerBooks />} />
<Route path="/olderBooks" element={<OlderBooks />} />
</CustomRoutes>
<Resource name="books" />
</Admin>
);
};
Tip: The storeKey is actually passed to the underlying useListController hook, which you can use directly for more complex scenarios. See the useListController doc for more info.
title
The default title for a list view is “[resource] list” (e.g. “Posts list”). Use the title prop to customize the List view title:
export const PostList = () => (
<List title="List of posts">
...
</List>
);
The title can be either a string or an element of your own.
sx: CSS API
The <List> component accepts the usual className prop but you can override many class names injected to the inner components by React-admin thanks to the sx property (as most Material UI components, see their documentation about it). This property accepts the following subclasses:
| Rule name | Description |
|---|---|
& .RaList-actions |
Applied to the actions container |
& .RaList-main |
Applied to the main container |
& .RaList-content |
Applied to the child component inside the main container |
& .RaList-noResults |
Applied to the component shown when there is no result |
Here is an example:
const PostList = () => (
<List
sx={{
backgroundColor: 'yellow',
'& .RaList-content': {
backgroundColor: 'red',
},
}}
>
...
</List>
);
Tip: The List component classes can also be customized for all instances of the component with its global css name RaList as describe here
Adding meta To The DataProvider Call
Use the queryOptions prop to pass a custom meta to the dataProvider.getList() call.
import { List } from 'react-admin';
const PostList = () => (
<List queryOptions={{ meta: { foo: 'bar' } }}>
...
</List>
);
Infinite Scroll Pagination
By default, the <List> component displays the first page of the list of records. To display the next page, the user must click on the “next” button. This is called “finite pagination”. An alternative is to display the next page automatically when the user scrolls to the bottom of the list. This is called “infinite pagination”.
To achieve infinite pagination, replace the <List> component with the <InfiniteList> component.
import {
- List,
+ InfiniteList,
Datagrid,
TextField,
DateField
} from 'react-admin';
const BookList = () => (
- <List>
+ <InfiniteList>
<Datagrid>
<TextField source="id" />
<TextField source="title" />
<DateField source="author" />
</Datagrid>
- </List>
+ </InfiniteList>
);
<InfiniteList> is a drop-in replacement for <List>. It accepts the same props, and uses the same view layout. Check the <InfiniteList> documentation for more information.
Live Updates
If you want to subscribe to live updates on the list of records (topic: resource/[resource]), use the <ListLive> component instead.
-import { List, Datagrid, TextField } from 'react-admin';
+import { Datagrid, TextField } from 'react-admin';
+import { ListLive } from '@react-admin/ra-realtime';
const PostList = () => (
- <List>
+ <ListLive>
<Datagrid>
<TextField source="title" />
</Datagrid>
- </List>
+ </ListLive>
);
The list will automatically update when a new record is created, or an existing record is updated or deleted.

