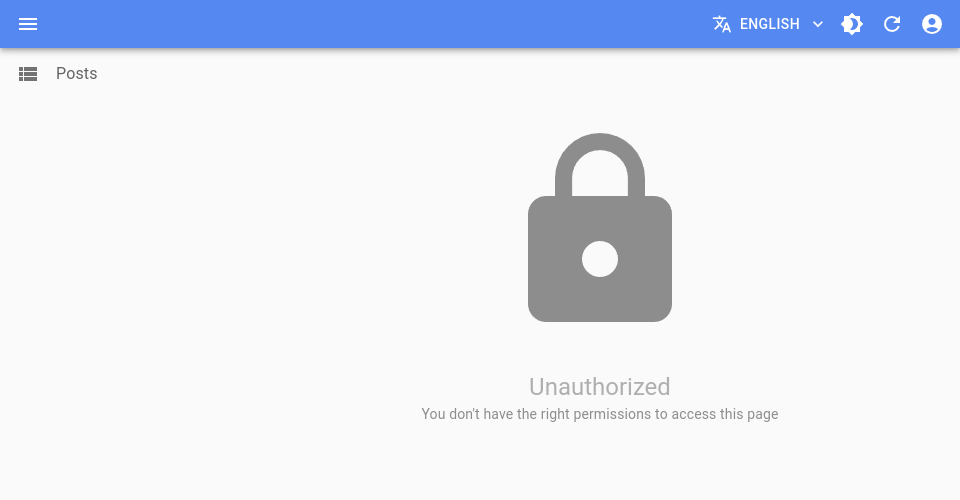
<CanAccess>
This component calls the authProvider.canAccess() method on mount for a provided resource and action (and optionally a record). It will only display its children when users are authorized. By default, it will redirect users to /authentication-error if an error occurs.
Usage
The following form only displays the role field if the user has the permission to perform the edit action on the users.role resource:
import { CanAccess, Edit, SelectInput, SimpleForm, TextInput } from 'react-admin';
const UserEdit = () => (
<Edit>
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="lastName">
<TextInput source="firstName">
<CanAccess action="edit" resource="users.role">
<SelectInput source="role" choices={['admin', 'user']}>
</CanAccess>
</SimpleForm>
</Edit>
);
<CanAccess> will call the authProvider.canAccess() method with the following parameters: { action: "edit", resource: "users.role", record: {} } where record will be the currently edited record.
Parameters
<CanAccess> expects the following props:
| Name | Required | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
action |
Required | string |
- | The action to check, e.g. ‘read’, ‘list’, ‘export’, ‘delete’, etc. |
resource |
string |
ResourceContext value | The resource to check, e.g. ‘users’, ‘comments’, ‘posts’, etc. | |
record |
object |
RecordContext value | The record to check. If passed, the child only renders if the user has access to that record, e.g. { id: 123, firstName: "John", lastName: "Doe" } |
|
loading |
ReactNode |
- | The element displayed while the canAccess call is pending |
|
accessDenied |
ReactNode |
- | The element displayed when users are denied access to the resource | |
error |
ReactNode |
- | The element displayed when an error occurs while calling authProvider.canAccess |
Securing Custom Routes
By default, there is no authentication or authorization control on custom routes. If you need to restrict access to a custom route, wrap the content with <CanAccess>. Remember to check the authentication status before with <Authenticated>:
import { Authenticated, CanAccess, AccessDenied } from 'react-admin';
export const LogsPage = () => (
<Authenticated>
<CanAccess resource="logs" action="read" accessDenied={<AccessDenied />}>
...
</CanAccess>
</Authenticated>
);
Use the <CustomRoutes> component to add custom routes to your admin.
import { Admin, CustomRoutes, Authenticated, CanAccess, AccessDenied, Layout } from 'react-admin';
import { Route } from 'react-router-dom';
import { LogsPage } from './LogsPage';
import { MyMenu } from './MyMenu';
const MyLayout = (props) => <Layout {...props} menu={MyMenu} />;
const App = () => (
<Admin authProvider={authProvider} layout={MyLayout}>
<CustomRoutes>
<Route path="/logs" element={<LogsPage />} />
</CustomRoutes>
</Admin>
);
Remember to also wrap your custom menu items with <CanAccess> to hide the menu items if the user doesn’t have access to the resource.
import { Menu, CanAccess } from "react-admin";
import SsidChartIcon from "@mui/icons-material/SsidChart";
export const MyMenu = () => (
<Menu>
<Menu.ResourceItems />
<CanAccess resource="logs" action="read">
<Menu.Item primaryText="Logs" to="/logs" leftIcon={<SsidChartIcon />} />
</CanAccess>
</Menu>
);
Note: You don’t need to use <CanAccess> on the core react-admin page components (<List>, <Create>, <Edit>, <Show>) because they already have built-in access control.
Note: You don’t need to use <Authenticated> on custom pages if your admin uses requireAuth.
Access Denied Message
By default, <CanAccess> renders nothing when the user doesn’t have access to the resource.
On custom pages, it’s preferable to show an error message instead. Set the accessDenied prop to render a custom component in case of access denial:
import { Authenticated, CanAccess, AccessDenied } from 'react-admin';
export const LogsPage = () => (
<Authenticated>
<CanAccess resource="logs" action="read" accessDenied={<AccessDenied />}>
...
</CanAccess>
</Authenticated>
);