<ReferenceManyField>
<ReferenceManyField> is useful for displaying a list of related records via a one-to-many relationship, when the foreign key is carried by the referenced resource.
This component fetches a list of referenced records by a reverse lookup of the current record.id in the target field of another resource (using the dataProvider.getManyReference() REST method), and puts them in a ListContext. Its children can then use the data from this context. The most common case is to use <SingleFieldList> or <DataTable> as child.
Tip: If the relationship is materialized by an array of ids in the initial record, use the <ReferenceArrayField> component instead.
Tip: To edit the records of a one-to-many relationship, use the <ReferenceManyInput> component.
Usage
For instance, if an author has many books, and each book resource exposes an author_id field:
┌────────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐
│ authors │ │ books │
│----------------│ │--------------│
│ id │───┐ │ id │
│ first_name │ └──╼│ author_id │
│ last_name │ │ title │
│ date_of_birth │ │ published_at │
└────────────────┘ └──────────────┘
<ReferenceManyField> can render the titles of all the books by a given author.
import { Show, SimpleShowLayout, ReferenceManyField, DataTable, TextField, DateField } from 'react-admin';
const AuthorShow = () => (
<Show>
<SimpleShowLayout>
<TextField source="first_name" />
<TextField source="last_name" />
<ReferenceManyField reference="books" target="author_id" label="Books">
<DataTable>
<DataTable.Col source="title" />
<DataTable.Col source="published_at" field={DateField} />
</DataTable>
</ReferenceManyField>
</SimpleShowLayout>
</Show>
);
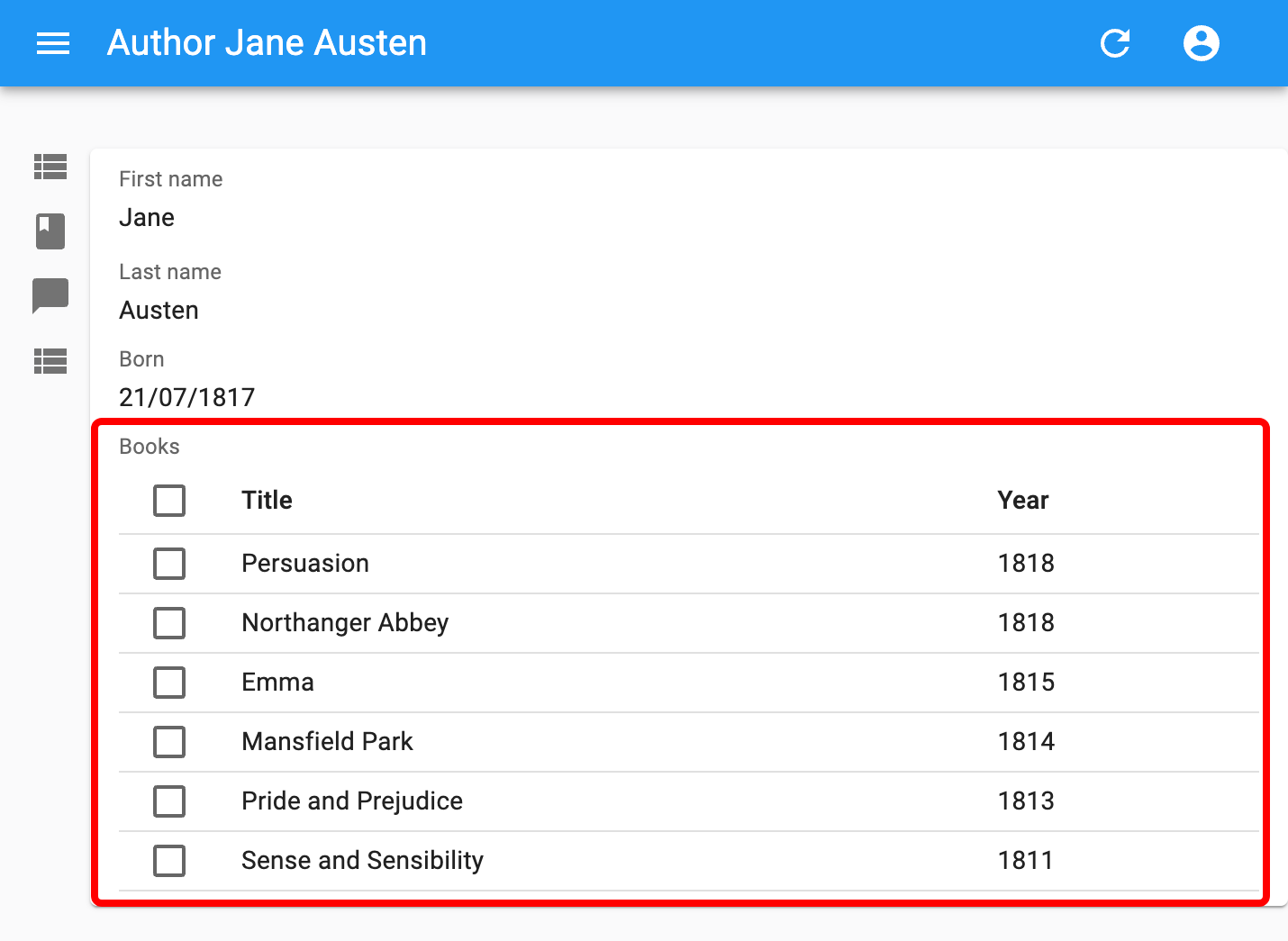
<ReferenceManyField> accepts a reference attribute, which specifies the resource to fetch for the related record. It also accepts a source attribute which defines the field containing the value to look for in the target field of the referenced resource. By default, this is the id of the resource (authors.id in the previous example).
You can also use <ReferenceManyField> in a list, e.g. to display the authors of the comments related to each post in a list by matching post.id to comment.post_id:
import { List, DataTable, ChipField, ReferenceManyField, SingleFieldList } from 'react-admin';
export const PostList = () => (
<List>
<DataTable>
<DataTable.Col source="id" />
<DataTable.Col source="title" />
<DataTable.Col label="Comments by">
<ReferenceManyField reference="comments" target="post_id">
<SingleFieldList>
<ChipField source="author.name" />
</SingleFieldList>
</ReferenceManyField>
</DataTable.Col>
<DataTable.Col>
<EditButton />
</DataTable.Col>
</DataTable>
</List>
);
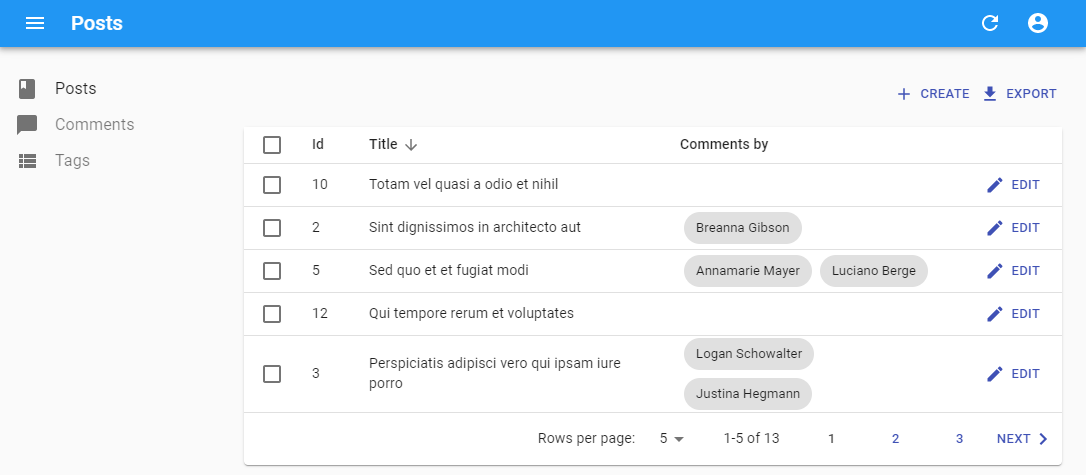
This example leverages <SingleFieldList> to display an inline list using only one field for each of the referenced records.
Props
| Prop | Required | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
reference |
Required | string |
- | The name of the resource for the referenced records, e.g. ‘books’ |
target |
Required | string |
- | Target field carrying the relationship on the referenced resource, e.g. ‘user_id’ |
children |
Optional * | Element |
- | One or several elements that render a list of records based on a ListContext |
render |
Optional * | (listContext) => Element |
- | Function that receives a ListContext and render elements |
debounce |
Optional | number |
500 | debounce time in ms for the setFilters callbacks |
empty |
Optional | ReactNode |
- | Element to display when there are no related records. |
error |
Optional | ReactNode |
- | The component to render when an error occurs while fetching the related records |
filter |
Optional | Object |
- | Filters to use when fetching the related records, passed to getManyReference() |
exporter |
Optional | function |
default Exporter |
The function called by export buttons in the list context |
loading |
Optional | ReactNode |
- | The component to render while fetching the related records |
offline |
Optional | ReactNode |
- | Element to display when there are no related records because of lack of network connectivity. |
pagination |
Optional | Element |
- | Pagination element to display pagination controls. empty by default (no pagination) |
perPage |
Optional | number |
25 | Maximum number of referenced records to fetch |
queryOptions |
Optional | UseQuery Options |
{} |
react-query options for the getMany query |
sort |
Optional | { field, order } |
{ field: 'id', order: 'DESC' } |
Sort order to use when fetching the related records, passed to getManyReference() |
source |
Optional | string |
id |
Target field carrying the relationship on the source record (usually ‘id’) |
storeKey |
Optional | string |
- | The key to use to store the records selection state |
* You must provide either children or render.
<ReferenceManyField> also accepts the common field props, except emptyText (use the child empty prop instead).
children
<ReferenceManyField> renders its children inside a ListContext. This means you can use any component that uses a ListContext:
<SingleFieldList><DataTable><Datagrid><SimpleList><EditableDatagrid><Calendar>- Or a component of your own (check the
<WithListContext>and theuseListContextchapters to learn how).
For instance, use a <DataTable> to render the related records in a table:
import { Show, SimpleShowLayout, TextField, ReferenceManyField, DataTable, DateField } from 'react-admin';
export const AuthorShow = () => (
<Show>
<SimpleShowLayout>
<TextField source="first_name" />
<TextField source="last_name" />
<DateField label="Born" source="dob" />
<ReferenceManyField label="Books" reference="books" target="author_id">
<DataTable>
<DataTable.Col source="title" />
<DataTable.Col source="published_at" field={DateField} />
</DataTable>
</ReferenceManyField>
</SimpleShowLayout>
</Show>
);
Alternatively, you can use the render prop to render the related records in a custom way:
import { Show, SimpleShowLayout, TextField, ReferenceManyField, DateField } from 'react-admin';
export const AuthorShow = () => (
<Show>
<SimpleShowLayout>
<TextField source="first_name" />
<TextField source="last_name" />
<DateField label="Born" source="dob" />
<ReferenceManyField
label="Books"
reference="books"
target="author_id"
render={({ data }) => (
<ul>
{data.map(book => (
<li key={book.id}>{book.title}</li>
))}
</ul>
)}
/>
</SimpleShowLayout>
</Show>
);
debounce
By default, <ReferenceManyField> does not refresh the data as soon as the user enters data in the filter form. Instead, it waits for half a second of user inactivity (via lodash.debounce) before calling the dataProvider on filter change. This is to prevent repeated (and useless) calls to the API.
You can customize the debounce duration in milliseconds - or disable it completely - by passing a debounce prop to the <ReferenceManyField> component:
// wait 1 seconds instead of 500 milliseconds before calling the dataProvider
const PostCommentsField = () => (
<ReferenceManyField debounce={1000}>
...
</ReferenceManyField>
);
empty
Use empty to customize the text displayed when the related record is empty.
<ReferenceManyField
reference="books"
target="author_id"
empty="no books"
>
...
</ReferenceManyField>
empty also accepts a translation key.
<ReferenceManyField
reference="books"
target="author_id"
empty="resources.authors.fields.books.empty"
>
...
</ReferenceManyField>
empty also accepts a ReactNode.
<ReferenceManyField
reference="books"
target="author_id"
empty={<CreateButton resource="books" />}
>
...
</ReferenceManyField>
error
By default, <ReferenceManyField> renders its children when an error occurs while fetching the related records. You can customize what is rendered by providing your own component via the error prop:
import { ReferenceManyField, Show, SimpleShowLayout } from 'react-admin';
export const AuthorShow = () => (
<Show>
<SimpleShowLayout>
<ReferenceManyField
reference="books"
target="author_id"
error={<p>Error loading books. Please try again.</p>}
>
...
</ReferenceManyField>
</SimpleShowLayout>
</Show>
);
You can also have <ReferenceManyField> render nothing in that case by setting the prop to null:
<ReferenceManyField
reference="books"
target="author_id"
error={null}
>
...
</ReferenceManyField>
filter: Permanent Filter
You can filter the query used to populate the possible values. Use the filter prop for that.
<ReferenceManyField
reference="comments"
target="post_id"
filter={{ is_published: true }}
>
...
</ReferenceManyField>
Filtering The References
You can add filters to <ReferenceManyField> by adding <FilterForm> and <FilterButton>:
const filters = [<TextInput source="q" label="Search" />];
const AuthorEdit = () => (
<Edit>
<SimpleForm>
<ReferenceManyField reference="comments" target="post_id">
<FilterButton filters={filters}/>
<FilterForm filters={filters}/>
<DataTable>
...
</DataTable>
</ReferenceManyField>
</SimpleForm>
</Edit>
);
label
By default, <SimpleShowLayout>, <DataTable> and other layout components infer the label of a field based on its source. For a <ReferenceManyField>, the source defaults to id, so this may not be what you expect:
{/* default label is 'Id', or the translation of 'resources.authors.fields.id' if it exists */}
<ReferenceManyField reference="books" target="author_id">
<DataTable>
<DataTable.Col source="title" />
<DataTable.Col source="published_at" field={DateField} />
</DataTable>
</ReferenceManyField>
That’s why you often need to set an explicit label on a <ReferenceField>:
<ReferenceManyField label="Books" reference="books" target="author_id">
<DataTable>
<DataTable.Col source="title" />
<DataTable.Col source="published_at" field={DateField} />
</DataTable>
</ReferenceManyField>
React-admin uses the i18n system to translate the label, so you can use translation keys to have one label for each language supported by the interface:
<ReferenceManyField label="resources.authors.fields.books" reference="books" target="author_id">
<DataTable>
<DataTable.Col source="title" />
<DataTable.Col source="published_at" field={DateField} />
</DataTable>
</ReferenceManyField>
loading
By default, <ReferenceManyField> renders its children while fetching the related records. You can customize what is rendered by providing your own component via the loading prop:
import { ReferenceManyField, Show, SimpleShowLayout } from 'react-admin';
import { CircularProgress } from '@mui/material';
export const AuthorShow = () => (
<Show>
<SimpleShowLayout>
<ReferenceManyField
reference="books"
target="author_id"
loading={<CircularProgress />}
>
...
</ReferenceManyField>
</SimpleShowLayout>
</Show>
);
You can also have <ReferenceManyField> render nothing in that case by setting the prop to null:
<ReferenceManyField
reference="books"
target="author_id"
loading={null}
>
...
</ReferenceManyField>
offline
By default, <ReferenceManyField> renders the <Offline variant="inline"> when there is no connectivity and the records haven’t been cached yet. You can provide your own component via the offline prop:
<ReferenceManyField
reference="books"
target="author_id"
offline="Offline, could not load data"
>
...
</ReferenceManyField>
offline also accepts a ReactNode.
<ReferenceManyField
reference="books"
target="author_id"
empty={<Alert severity="warning">Offline, could not load data</Alert>}
>
...
</ReferenceManyField>
Tip: If the records are in the Tanstack Query cache but you want to warn the user that they may see an outdated version, you can use the <IsOffline> component:
<ReferenceManyField
reference="books"
target="author_id"
empty={<Alert severity="warning">Offline, could not load data</Alert>}
>
<IsOffline>
<Alert severity="warning">
You are offline, the data may be outdated
</Alert>
</IsOffline>
...
</ReferenceManyField>
pagination
If you want to allow users to paginate the list, pass a <Pagination> element as the pagination prop:
import { Pagination } from 'react-admin';
<ReferenceManyField pagination={<Pagination />} reference="comments" target="post_id">
...
</ReferenceManyField>
perPage
By default, react-admin restricts the possible values to 25 and displays no pagination control. You can change the limit by setting the perPage prop:
<ReferenceManyField perPage={10} reference="comments" target="post_id">
...
</ReferenceManyField>
queryOptions
Use the queryOptions prop to pass options to the dataProvider.getMany() query that fetches the referenced record.
For instance, to pass a custom meta:
<ReferenceManyField queryOptions={{ meta: { foo: 'bar' } }} />
reference
The name of the resource to fetch for the related records.
For instance, if you want to display the books of a given author, the reference name should be books:
<ReferenceManyField label="Books" reference="books" target="author_id">
<DataTable>
<DataTable.Col source="title" />
<DataTable.Col source="published_at" field={DateField} />
</DataTable>
</ReferenceManyField>
render
Alternatively to children, you can pass a render prop to <ReferenceManyField>. It will receive the ListContext as its argument, and should return a React node.
This allows to inline the render logic for the list of related records.
<ReferenceManyField
reference="books"
target="author_id"
render={({ isPending, error, data }) => {
if (isPending) {
return <p>Loading...</p>;
}
if (error) {
return <p className="error">{error.toString()}</p>;
}
return (
<p>
{data.map((author, index) => (
<li key={index}>{author.name}</li>
))}
</p>
);
}}
/>
sort
By default, it orders the possible values by id desc. You can change this order by setting the sort prop (an object with field and order properties).
<ReferenceManyField
target="post_id"
reference="comments"
sort={{ field: 'created_at', order: 'DESC' }}
>
...
</ReferenceManyField>
source
By default, ReferenceManyField uses the id field as target for the reference. If the foreign key points to another field of your record, you can select it with the source prop.
<ReferenceManyField
target="post_id"
reference="comments"
source="_id"
>
...
</ReferenceManyField>
storeKey
By default, react-admin stores the reference list selection state in localStorage so that users can come back to the list and find it in the same state as when they left it. React-admin uses the main resource, record id and reference resource as the identifier to store the selection state (under the key ${resource}.${record.id}.${reference}.selectedIds).
If you want to display multiple lists of the same reference and keep distinct selection states for each one, you must give each list a unique storeKey property.
In the example below, both lists use the same reference (‘books’), but their selection states are stored separately (under the store keys 'authors.1.books.selectedIds' and 'custom.selectedIds' respectively). This allows to use both components in the same page, each having its own state.
<Stack direction="row" spacing={2}>
<ReferenceManyField
reference="books"
target="author_id"
queryOptions={{
meta: { foo: 'bar' },
}}
>
<DataTable>
<DataTable.Col source="title" />
</DataTable>
</ReferenceManyField>
<ReferenceManyField
reference="books"
target="author_id"
queryOptions={{
meta: { foo: 'bar' },
}}
storeKey="custom"
>
<DataTable>
<DataTable.Col source="title" />
</DataTable>
</ReferenceManyField>
</Stack>
target
Name of the field carrying the relationship on the referenced resource. For instance, if an author has many books, and each book resource exposes an author_id field, the target would be author_id.
<ReferenceManyField label="Books" reference="books" target="author_id">
<DataTable>
<DataTable.Col source="title" />
<DataTable.Col source="published_at" field={DateField} />
</DataTable>
</ReferenceManyField>
Rendering Only One Record
Although you are in a one-to-many relationship, you may want to render only one record. For instance, in a book with several reviews, you may want to display only the last. Or, for a product with many prices, you may want to display only the one in euros.
In these cases, use the <ReferenceOneField> component instead of <ReferenceManyField>.
<ReferenceOneField
label="Latest review"
reference="book_reviews"
target="book_id"
sort={{ field: "createdAt", order: "DESC" }}
>
<RatingField />
<TextField source="body" />
</ReferenceOneField>
<ReferenceOneField
label="Price (€)"
reference="product_prices"
target="product_id"
filter={{ currency: "EUR" }}
>
<NumberField source="price" />
</ReferenceOneField>
Adding or editing a related record
To allow users to create or edit a record without leaving the current view, use the <CreateInDialogButton> or the <EditInDialogButton> component.
import { Edit, SimpleForm, TextInput, ReferenceManyField, WithRecord, DataTable } from 'react-admin';
import { CreateInDialogButton, EditInDialogButton } from "@react-admin/ra-form-layout";
const EmployerEdit = () => (
<Edit>
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="name" />
<TextInput source="address" />
<TextInput source="city" />
<ReferenceManyField
target="employer_id"
reference="customers"
>
<WithRecord
render={record => (
<CreateInDialogButton
record={{ employer_id: record.id }}
>
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="first_name" />
<TextInput source="last_name" />
</SimpleForm>
</CreateInDialogButton>
)}
/>
<DataTable>
<DataTable.Col source="first_name" />
<DataTable.Col source="last_name" />
<DataTable.Col>
<EditInDialogButton>
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="first_name" />
<TextInput source="last_name" />
</SimpleForm>
</EditInDialogButton>
</DataTable.Col>
</DataTable>
</ReferenceManyField>
</SimpleForm>
</Edit>
)

