<ReferenceInput>
Use <ReferenceInput> for foreign-key values, for instance, to edit the company_id of a contact resource.
Usage
For instance, a contact record has a company_id field, which is a foreign key to a company record.
┌──────────────┐ ┌────────────┐
│ contacts │ │ companies │
│--------------│ │------------│
│ id │ ┌───│ id │
│ first_name │ │ │ name │
│ last_name │ │ │ address │
│ company_id │───┘ └────────────┘
└──────────────┘
To make the company_id for a contact editable, use the following syntax:
import { Edit, SimpleForm, TextInput, ReferenceInput } from 'react-admin';
const ContactEdit = () => (
<Edit>
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="first_name" />
<TextInput source="last_name" />
<TextInput source="title" />
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies" />
</SimpleForm>
</Edit>
);
<ReferenceInput> requires a source and a reference prop.
<ReferenceInput> uses the foreign key value to fetch the related record. It also grabs the list of possible choices for the field. For instance, if the ContactEdit component above is used to edit the following contact:
{
id: 123,
first_name: 'John',
last_name: 'Doe',
company_id: 456
}
Then <ReferenceInput> will issue the following queries:
dataProvider.getMany('companies', { ids: [456] });
dataProvider.getList('companies', {
filter: {},
sort: { field: 'id', order: 'DESC' },
pagination: { page: 1, perPage: 25 }
});
<ReferenceInput> renders an <AutocompleteInput> to let the user select the related record. Users can narrow down the choices by typing a search term in the input. This modifies the query sent to the dataProvider as follows:
dataProvider.getList('companies', {
filter: { q: ['search term'] },
sort: { field: 'id', order: 'DESC' },
pagination: { page: 1, perPage: 25 }
});
See Customizing the filter query below for more information about how to change filter prop based on the <AutocompleteInput> search term.
You can tweak how <ReferenceInput> fetches the possible values using the page, perPage, sort, and filter props.
You can replace the default <AutocompleteInput> by another choice input. To do so, pass the choice input component as <ReferenceInput> child. For instance, to use a <SelectInput>:
import { ReferenceInput, SelectInput } from 'react-admin';
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies">
<SelectInput />
</ReferenceInput>
See the children section for more details.
Props
| Prop | Required | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
source |
Required | string |
- | Name of the entity property to use for the input value |
reference |
Required | string |
’’ | Name of the reference resource, e.g. ‘companies’. |
children |
Optional | ReactNode |
<Autocomplete Input/> |
The actual selection component |
enableGet Choices |
Optional | ({q: string}) => boolean |
() => true |
Function taking the filterValues and returning a boolean to enable the getList call. |
filter |
Optional | Object |
{} |
Permanent filters to use for getting the suggestion list |
label |
Optional | string |
- | Useful only when ReferenceInput is in a Filter array, the label is used as the Filter label. |
page |
Optional | number |
1 | The current page number |
perPage |
Optional | number |
25 | Number of suggestions to show |
offline |
Optional | ReactNode |
- | What to render when there is no network connectivity when loading the record |
queryOptions |
Optional | UseQueryOptions |
{} |
react-query client options |
sort |
Optional | { field: String, order: 'ASC' or 'DESC' } |
{ field:'id', order:'DESC' } |
How to order the list of suggestions |
Note: <ReferenceInput> doesn’t accept the common input props (like label) ; it is the responsibility of the child component to apply them. The same goes for validation: pass validate to the child input (<AutocompleteInput>, <SelectInput>, <RadioButtonGroupInput>, etc.), not to <ReferenceInput>. This also applies to other reference inputs like <ReferenceArrayInput>.
children
By default, <ReferenceInput> renders an <AutocompleteInput> to let end users select the reference record.
You can pass a child component to customize the way the reference selector is displayed.
For instance, to customize the input label, set the label prop on the child component:
import { ReferenceInput, AutocompleteInput } from 'react-admin';
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies">
<AutocompleteInput label="Employer" />
</ReferenceInput>
You can also use <SelectInput> or <RadioButtonGroupInput> instead of <AutocompleteInput>.
import { ReferenceInput, SelectInput } from 'react-admin';
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies">
<SelectInput />
</ReferenceInput>
If your users need to compare multiple fields before selecting a record, you can use <DataTableInput>:
import { DataTableInput } from '@react-admin/ra-form-layout';
import { DataTable, ReferenceInput } from 'react-admin';
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies">
<DataTableInput>
<DataTable.Col source="company_name" />
<DataTable.Col source="country" />
<DataTable.Col source="city" />
<DataTable.Col source="industry" />
</DataTableInput>
</ReferenceInput>
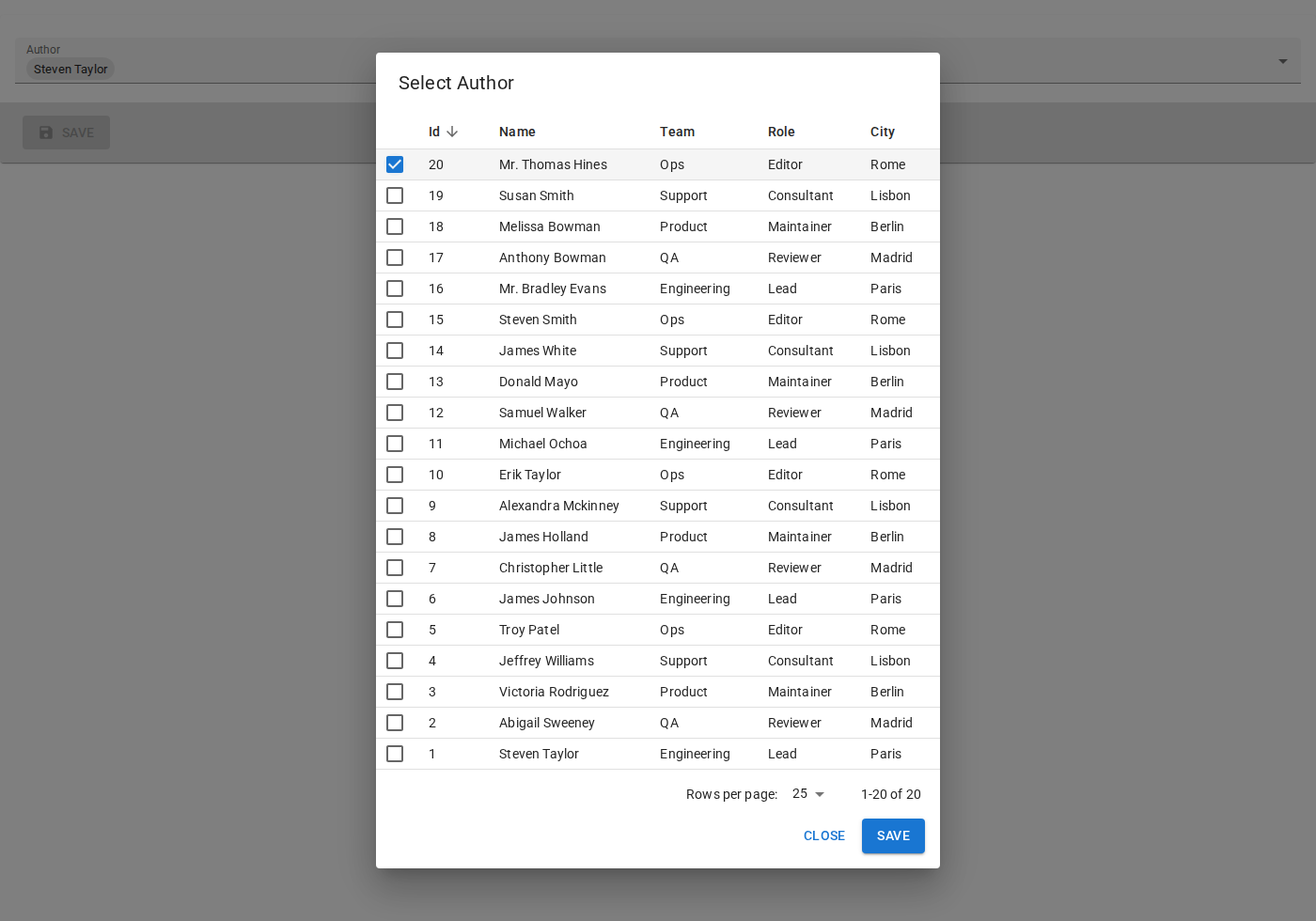
You can even use a component of your own as child, provided it detects a ChoicesContext is available and gets their choices from it.
The choices context value can be accessed with the useChoicesContext hook.
enableGetChoices
You can make the getList() call lazy by using the enableGetChoices prop. This prop should be a function that receives the filterValues as parameter and return a boolean. This can be useful when using an AutocompleteInput on a resource with a lot of data. The following example only starts fetching the options when the query has at least 2 characters:
<ReferenceInput
source="company_id"
reference="companies"
enableGetChoices={({ q }) => q && q.length >= 2}
/>
filter
You can filter the query used to populate the possible values. Use the filter prop for that.
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies" filter={{ is_published: true }} />
Note: When users type a search term in the <AutocompleteInput>, this doesn’t affect the filter prop. Check the Customizing the filter query section below for details on how that filter works.
label
In an <Edit> or <Create> view, the label prop has no effect. <ReferenceInput> has no label, it simply renders its child (an <AutocompleteInput> by default). If you need to customize the label, set the label prop on the child element:
import { ReferenceInput, AutocompleteInput } from 'react-admin';
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies">
<AutocompleteInput label="Employer" />
</ReferenceInput>
In a Filter form, react-admin uses the label prop to set the Filter label. So in this case, the label prop is not ignored, but you also have to set it on the child input.
const filters = [
<ReferenceInput label="Employer" source="company_id" reference="companies">
<AutocompleteInput label="Employer" />
</ReferenceInput>,
];
offline
<ReferenceInput> can display a custom message when the referenced record is missing because there is no network connectivity, thanks to the offline prop.
<ReferenceInput source="user_id" reference="users" offline="No network, could not fetch data" />
<ReferenceInput> renders the offline element when:
- the referenced record is missing (no record in the
userstable with the rightuser_id), and - there is no network connectivity
You can pass either a React element or a string to the offline prop:
<ReferenceInput source="user_id" reference="users" offline={<span>No network, could not fetch data</span>} />
<ReferenceInput source="user_id" reference="users" offline="No network, could not fetch data" />
parse
By default, children of <ReferenceInput> transform the empty form value (an empty string) into null before passing it to the dataProvider.
If you want to change this behavior, you have to pass a custom parse prop to the <ReferenceInput> child component, because <ReferenceInput> doesn’t have a parse prop. It is the responsibility of the child component to parse the input value.
For instance, if you want to transform an option value before submission, and the selection control is an <AutocompleteInput> (the default), set the <AutocompleteInput parse> prop as follows:
import { ReferenceInput, AutocompleteInput } from 'react-admin';
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies">
<AutocompleteInput parse={value => value === 'not defined' ? null : value} />
</ReferenceInput>
The same goes if the child is a <SelectInput>:
import { ReferenceInput, SelectInput } from 'react-admin';
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies">
<SelectInput parse={value => value === 'not defined' ? undefined : null} />
</ReferenceInput>
perPage
By default, <ReferenceInput> fetches only the first 25 values. You can extend this limit by setting the perPage prop.
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies" perPage={100} />
This prop is mostly useful when using <SelectInput> or <RadioButtonGroupInput> as child, as the default <AutocompleteInput> child allows to filter the possible choices with a search input.
reference
The name of the reference resource. For instance, in a contact form, if you want to edit the contact employer, the reference should be “companies”.
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies" />
<ReferenceInput> will use the reference resource recordRepresentation to display the selected record and the list of possible records. So for instance, if the companies resource is defined as follows:
<Resource name="companies" recordRepresentation="name" />
Then <ReferenceInput> will display the company name in the input and in the list of possible values.
You can override this default by specifying the optionText prop in the child component. For instance, for an <AutocompleteInput>:
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies">
<AutocompleteInput optionText="reference" />
</ReferenceInput>
queryOptions
Use the queryOptions prop to pass options to the dataProvider.getList() query that fetches the possible choices.
For instance, to pass a custom meta:
<ReferenceInput
source="company_id"
reference="companies"
queryOptions={{ meta: { foo: 'bar' } }}
/>
sort
By default, <ReferenceInput> orders the possible values by id desc.
You can change this order by setting the sort prop (an object with field and order properties).
<ReferenceInput
source="company"
reference="companies"
sort={{ field: 'name', order: 'ASC' }}
/>
source
The name of the property in the record that contains the identifier of the selected record.
For instance, if a contact contains a reference to a company via a company_id property:
{
id: 456,
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Doe",
company_id: 12,
}
Then to display a selector for the contact company, you should call <ReferenceInput> as follows:
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies" />
Validation
<ReferenceInput> doesn’t accept a validate prop. Put validation on the child input instead (<AutocompleteInput>, <SelectInput>, <RadioButtonGroupInput>, etc.).
import { ReferenceInput, SelectInput, required } from 'react-admin';
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies">
<SelectInput validate={required()} />
</ReferenceInput>
Transforming The Input Value
By default, children of <ReferenceInput> transform null values from the dataProvider into empty strings.
If you want to change this behavior, you have to pass a custom format prop to the <ReferenceInput> child component, because <ReferenceInput> doesn’t have a format prop. It is the responsibility of the child component to format the input value.
For instance, if you want to transform an option value before rendering, and the selection control is an <AutocompleteInput> (the default), set the <AutocompleteInput format> prop as follows:
import { ReferenceInput, AutocompleteInput } from 'react-admin';
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies">
<AutocompleteInput format={value => value == null ? 'not defined' : value} />
</ReferenceInput>
The same goes if the child is a <SelectInput>:
import { ReferenceInput, SelectInput } from 'react-admin';
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies">
<SelectInput format={value => value === undefined ? 'not defined' : null} />
</ReferenceInput>
Customizing The Filter Query
By default, <ReferenceInput> renders an <AutocompleteInput>, which lets users type a search term to filter the possible values. <ReferenceInput> calls dataProvider.getList() using the search term as filter, using the format filter: { q: [search term] }.
If you want to customize the conversion between the search term and the query filter to match the filtering capabilities of your API, use the <AutocompleteInput filterToQuery> prop.
const filterToQuery = searchText => ({ name_ilike: `%${searchText}%` });
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies">
<AutocompleteInput filterToQuery={filterToQuery} />
</ReferenceInput>
Creating a New Reference
When users don’t find the reference they are looking for in the list of possible values, they need to create a new reference. If they have to quit the current form to create the reference, they may lose the data they have already entered. So a common feature for <ReferenceInput> is to let users create a new reference on the fly.
Children of <ReferenceInput> (<AutocompleteInput>, <SelectInput>, etc.) allow the creation of new choices via the onCreate prop. This displays a new “Create new” option in the list of choices. You can leverage this capability to create a new reference record.
The following example is a contact edition form using a <ReferenceInput> to select the contact company. Its child <AutocompleteInput onCreate> allows to create a new company on the fly if it doesn’t exist yet.
export const ContactEdit = () => {
const [create] = useCreate();
const notify = useNotify();
const handleCreateCompany = async (companyName?: string) => {
if (!companyName) return;
try {
const newCompany = await create(
'companies',
{ data: { name: companyName } },
{ returnPromise: true }
);
return newCompany;
} catch (error) {
notify('An error occurred while creating the company', {
type: 'error',
});
throw(error);
}
};
return (
<Edit>
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="first_name" />
<TextInput source="last_name" />
<ReferenceInput source="company_id" reference="companies">
<AutocompleteInput onCreate={handleCreateCompany} />
</ReferenceInput>
</SimpleForm>
</Edit>
);
};
In the example above, the handleCreateCompany function creates a new company with the name provided by the user, and returns it so that <AutocompleteInput> selects it.
You can learn more about the onCreate prop in the documentation of the selection input components:
If you need to ask the user for more details about the new reference, you display a custom element (e.g. a dialog) when the user selects the “Create” option. use the create prop for that instead of onCreate.
You can learn more about the create prop in the documentation of the selection input components:
Tree Structure
If the reference resource is a tree, use <ReferenceNodeInput> instead of <ReferenceInput>.
For instance, to edit the category of a product and let the user choose the category in a tree:
import { Edit, SimpleForm, TextInput } from 'react-admin';
import { ReferenceNodeInput } from '@react-admin/ra-tree';
const ProductEdit = () => (
<Edit>
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="id" disabled />
<TextInput source="name" />
<ReferenceNodeInput
source="category_id"
reference="categories"
/>
</SimpleForm>
</Edit>
);
Performance
Why does <ReferenceInput> use the dataProvider.getMany() method with a single value [id] instead of dataProvider.getOne() to fetch the record for the current value?
Because when there may be many <ReferenceInput> for the same resource in a form (for instance when inside an <ArrayInput>), react-admin aggregates the calls to dataProvider.getMany() into a single one with [id1, id2, ...].
This speeds up the UI and avoids hitting the API too much.

