<AutocompleteInput>
To let users choose a value in a list using a dropdown with autocompletion, use <AutocompleteInput>.
It renders using Material UI’s <Autocomplete>.
This input allows editing record fields that are scalar values, e.g. 123, 'admin', etc.
Usage
In addition to the source, <AutocompleteInput> requires one prop: the choices listing the possible values.
import { AutocompleteInput } from 'react-admin';
<AutocompleteInput source="category" choices={[
{ id: 'tech', name: 'Tech' },
{ id: 'lifestyle', name: 'Lifestyle' },
{ id: 'people', name: 'People' },
]} />
By default, the possible choices are built from the choices prop, using:
- the
idfield as the option value, - the
namefield as the option text
The form value for the source must be the selected value, e.g.
{
id: 123,
title: 'Lorem Ipsum',
category: 'lifestyle',
}
Tip: React-admin includes other components to edit such values:
<SelectInput>renders a dropdown<RadioButtonGroupInput>renders a list of radio buttons
Tip: If you need to let users select more than one item in the list, check out the <AutocompleteArrayInput> component.
Tip: If users need to compare multiple fields before choosing (e.g. team, region, SLA, status), use <DataTableInput>.
Props
| Prop | Required | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
choices |
Optional | Object[] |
- |
List of items to autosuggest. Required if not inside a ReferenceInput. |
create |
Optional | Element |
- |
A React Element to render when users want to create a new choice |
createLabel |
Optional | string | ReactNode |
- | The label used as hint to let users know they can create a new choice. Displayed when the filter is empty. |
createItemLabel |
Optional | string | (filter: string) => ReactNode |
ra.action .create_item |
The label for the menu item allowing users to create a new choice. Used when the filter is not empty. |
debounce |
Optional | number |
250 |
The delay to wait before calling the setFilter function injected when used in a ReferenceInput. |
emptyText |
Optional | string |
'' |
The text to use for the empty element |
emptyValue |
Optional | any |
'' |
The value to use for the empty element |
filterToQuery |
Optional | string => Object |
q => ({ q }) |
How to transform the searchText into a parameter for the data provider |
isPending |
Optional | boolean |
false |
If true, the component will display a loading indicator. |
inputText |
Optional | Function |
- |
Required if optionText is a custom Component, this function must return the text displayed for the current selection. |
matchSuggestion |
Optional | Function |
- |
Required if optionText is a React element. Function returning a boolean indicating whether a choice matches the filter. (filter, choice) => boolean |
offline |
Optional | ReactNode |
- | What to render when there is no network connectivity when fetching the choices |
onChange |
Optional | Function |
- |
A function called with the new value, along with the selected record, when the input value changes |
onCreate |
Optional | Function |
- |
A function called with the current filter value when users choose to create a new choice. |
optionText |
Optional | function | ReactNode |
undefined | record Representation |
Field name of record to display in the suggestion item or function using the choice object as argument |
optionValue |
Optional | string |
id |
Field name of record containing the value to use as input value |
setFilter |
Optional | Function |
null |
A callback to inform the searchText has changed and new choices can be retrieved based on this searchText. Signature searchText => void. This function is automatically set up when using ReferenceInput. |
shouldRender Suggestions |
Optional | Function |
() => true |
A function that returns a boolean to determine whether or not suggestions are rendered. |
suggestionLimit |
Optional | number |
null |
Limits the numbers of suggestions that are shown in the dropdown list |
translateChoice |
Optional | boolean |
true |
Whether the choices should be translated |
<AutocompleteInput> also accepts the common input props.
choices
An array of objects that represents the possible suggestions. The objects must have at least two fields: one to use for the name, and the other to use for the value. By default, <AutocompleteInput> will use the id and name fields.
const choices = [
{ id: 'tech', name: 'Tech' },
{ id: 'lifestyle', name: 'Lifestyle' },
{ id: 'people', name: 'People' },
];
<AutocompleteInput source="category" choices={choices} />
If the choices have different keys, you can use optionText and optionValue to specify which fields to use for the name and value.
const choices = [
{ _id: 'tech', label: 'Tech' },
{ _id: 'lifestyle', label: 'Lifestyle' },
{ _id: 'people', label: 'People' },
];
<AutocompleteInput
source="category"
choices={choices}
optionText="label"
optionValue="_id"
/>
The choices are translated by default, so you can use translation identifiers as choices:
const choices = [
{ id: 'tech', name: 'myroot.categories.tech' },
{ id: 'lifestyle', name: 'myroot.categories.lifestyle' },
{ id: 'people', name: 'myroot.categories.people' },
];
You can opt-out of this translation by setting the translateChoice prop to false.
If you need to fetch the options from another resource, you’re usually editing a many-to-one or a one-to-one relationship. In this case, wrap the <AutocompleteInput> in a <ReferenceInput>. You don’t need to specify the choices prop - the parent component injects it based on the possible values of the related resource.
<ReferenceInput label="Author" source="author_id" reference="authors">
<AutocompleteInput />
</ReferenceInput>
See Selecting a foreign key below for more information.
You can also pass an array of strings for the choices:
const categories = ['tech', 'lifestyle', 'people'];
<AutocompleteInput source="category" choices={categories} />
// is equivalent to
const choices = categories.map(value => ({ id: value, name: value }));
<AutocompleteInput source="category" choices={choices} />
create
To allow users to add new options, pass a React element as the create prop. <AutocompleteInput> will then render a menu item at the bottom of the list, which will render the passed element when clicked.
import {
Create,
CreateBase,
SimpleForm,
ReferenceInput,
AutocompleteInput,
TextInput,
useCreateSuggestionContext
} from 'react-admin';
import CloseIcon from '@mui/icons-material/Close';
import {
Dialog,
DialogContent,
DialogTitle,
IconButton,
} from '@mui/material';
const BookCreate = () => (
<Create>
<SimpleForm>
<ReferenceInput reference="authors" source="author">
<AutocompleteInput
create={<CreateAuthor />}
/>
</ReferenceInput>
</SimpleForm>
</Create>
);
const CreateAuthor = () => {
const { filter, onCancel, onCreate } = useCreateSuggestionContext();
return (
<Dialog open onClose={onCancel}>
<DialogTitle sx={{ m: 0, p: 2 }}>Create Author</DialogTitle>
<IconButton
aria-label="close"
onClick={onCancel}
sx={theme => ({
position: 'absolute',
right: 8,
top: 8,
color: theme.palette.grey[500],
})}
>
<CloseIcon />
</IconButton>
<DialogContent sx={{ p: 0 }}>
<CreateBase
redirect={false}
resource="authors"
mutationOptions={{
onSuccess: onCreate,
}}
>
<SimpleForm defaultValues={{ name: filter }}>
<TextInput source="name" helperText={false} />
<TextInput source="language" helperText={false} autoFocus />
</SimpleForm>
</CreateBase>
</DialogContent>
</Dialog>
);
};
Tip: In development with React.StrictMode, you may run into an issue where the <AutocompleteInput> menu reopens after clicking the create item when the openOnFocus prop is set to true which is the default with React-admin. If that bothers you, set the openOnFocus prop to false.
If you want to customize the label of the “Create XXX” option, use the createItemLabel prop.
If you just need to ask users for a single string to create the new option, you can use the onCreate prop instead.
createLabel
When you set the create or onCreate prop, <AutocompleteInput> lets users create new options.
You can use the createLabel prop to render an additional (disabled) menu item at the bottom of the list, that will only appear when the input is empty, inviting users to start typing to create a new option.
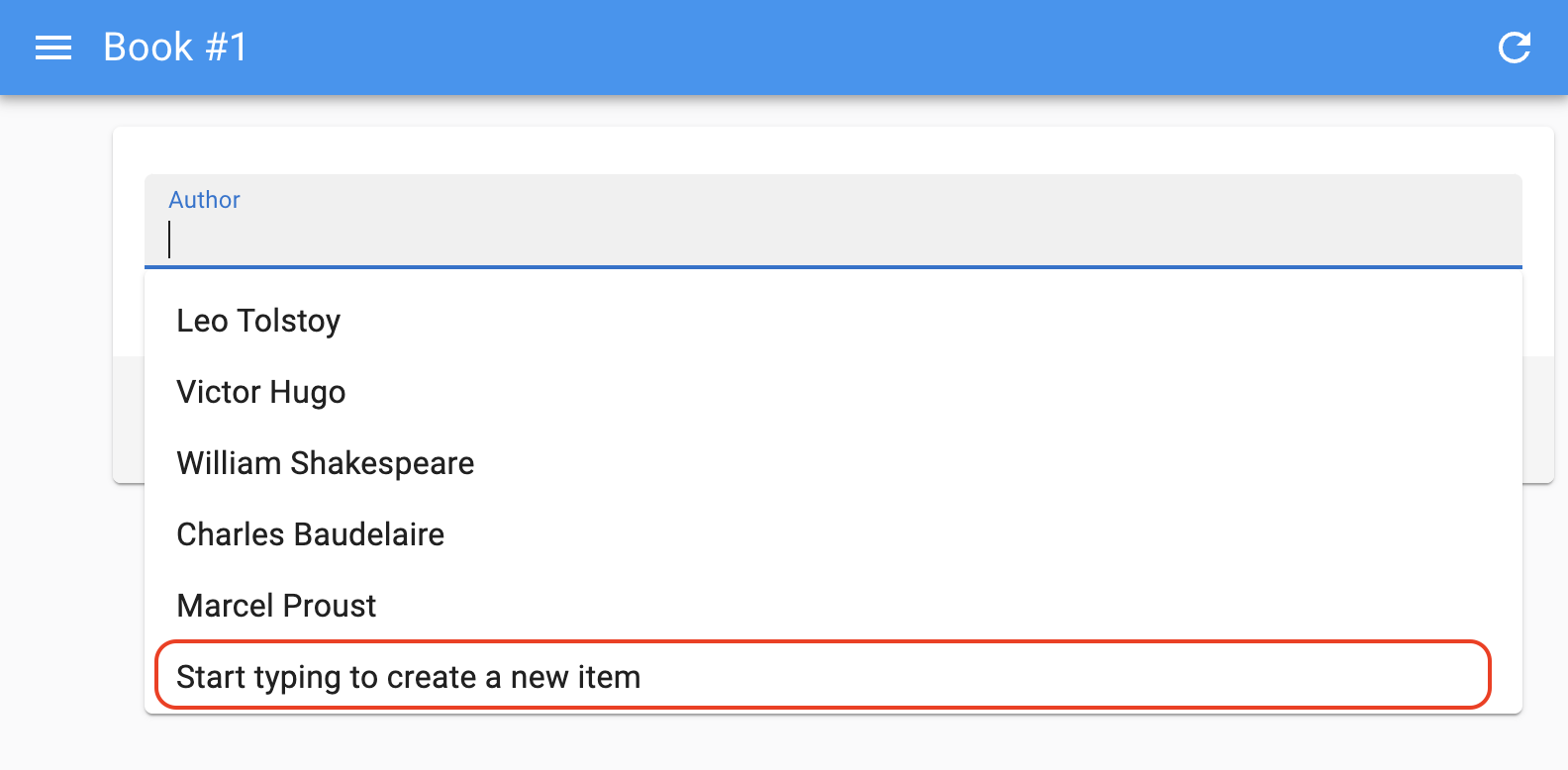
<AutocompleteInput
source="author"
choices={authors}
onCreate={onCreate}
createLabel="Start typing to create a new item"
/>
You can also use any React node as the create label.
<AutocompleteInput
source="author"
choices={authors}
onCreate={onCreate}
createLabel={
<Typography className="custom">
Start typing to create a new <strong>author</strong>
</Typography>
}
/>
createItemLabel
If you set the create or onCreate prop, <AutocompleteInput> lets users create new options. When the text entered by the user doesn’t match any option, the input renders a “Create XXX” menu item at the bottom of the list.
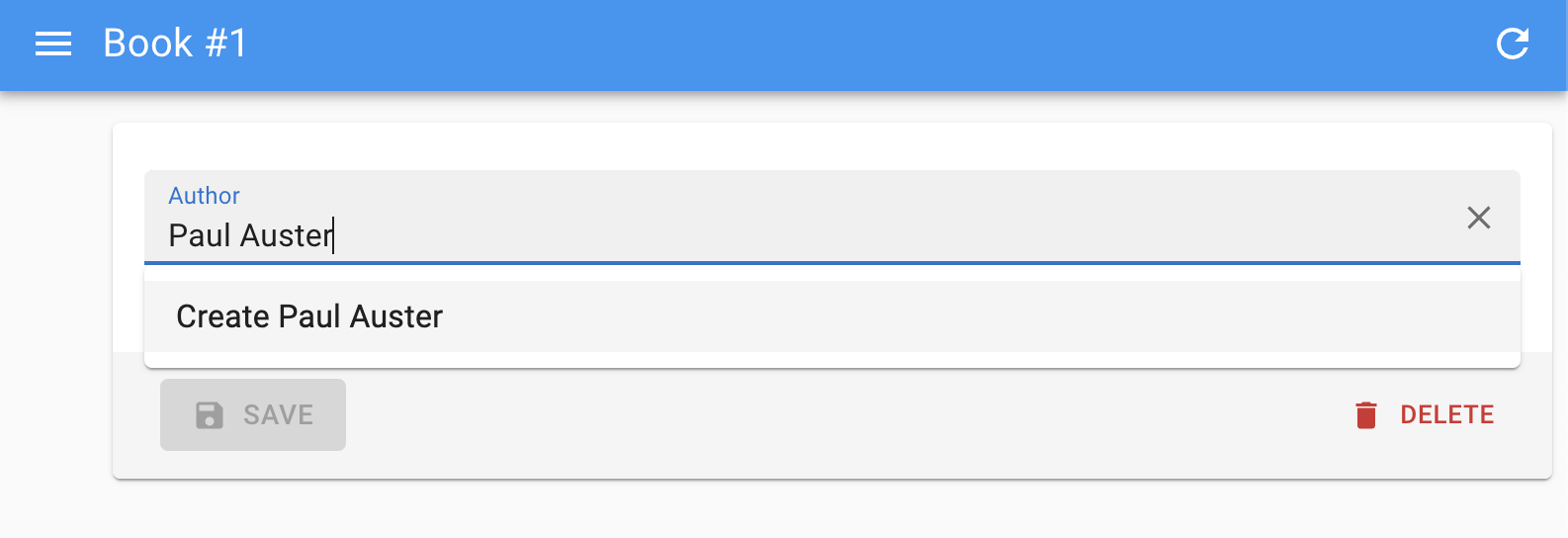
You can customize the label of that menu item by setting a custom translation for the ra.action.create_item key in the translation files.
Or, if you want to customize it just for this <AutocompleteInput>, use the createItemLabel prop:
<AutocompleteInput
source="author"
choices={authors}
onCreate={onCreate}
createItemLabel="Add a new author: %{item}"
/>
You can also define a function returning any rendered React node.
<AutocompleteInput
source="author"
choices={authors}
onCreate={onCreate}
createItemLabel={item => (
<Typography className="custom">
Create <Chip label={item} />
</Typography>
)}
/>
debounce
When used inside a <ReferenceInput>, <AutocompleteInput> will call dataProvider.getList() with the current input value as filter after a delay of 250ms. This is to avoid calling the API too often while users are typing their query.
This delay can be customized by setting the debounce prop.
<ReferenceInput label="Author" source="author_id" reference="authors">
<AutocompleteInput debounce={500} />
</ReferenceInput>
Tip: The signal Parameter section explains how to use the AbortSignal interface to abort the last API call and avoid parallel requests.
emptyText
If the input isn’t required (using validate={required()}), and you need a choice to represent the empty value, set emptyText prop and a choice will be added at the top, with its value as label.
<AutocompleteInput source="author_id" choices={choices} emptyText="No author" />
The emptyText prop accepts either a string or a React Element.
And if you want to hide that empty choice, make the input required.
<AutocompleteInput source="author_id" choices={choices} validate={required()} />
emptyValue
If the input isn’t required (using validate={required()}), users can select an empty choice. The default value for that empty choice is the empty string (''), or null if the input is inside a <ReferenceInput>.
You can override this value with the emptyValue prop.
<AutocompleteInput source="author_id" choices={choices} emptyValue={0} />
Tip: While you can set emptyValue to a non-string value (e.g. 0), you cannot use null or undefined, as it would turn the <AutocompleteInput> into an uncontrolled component. If you need the empty choice to be stored as null or undefined, use the parse prop to convert the default empty value (‘’) to null or undefined, or use the sanitizeEmptyValues prop on the Form component.
filterToQuery
When used inside a <ReferenceInput>, whenever users type a string in the autocomplete input, <AutocompleteInput> calls dataProvider.getList() using the string as filter, to return a filtered list of possible options from the reference resource. This filter is built using the filterToQuery prop.
By default, the filter is built using the q parameter. This means that if the user types the string ‘lorem’, the filter will be { q: 'lorem' }.
You can customize the filter by setting the filterToQuery prop. It should be a function that returns a filter object.
const filterToQuery = searchText => ({ name_ilike: `%${searchText}%` });
<ReferenceInput label="Author" source="author_id" reference="authors">
<AutocompleteInput filterToQuery={filterToQuery} />
</ReferenceInput>
isPending
When fetching choices from a remote API, the <AutocompleteInput> can’t be used until the choices are fetched. To let the user know, you can pass the isPending prop to <AutocompleteInput>. This displays a loading message in the autocomplete box while the choices are being fetched.
import { useGetList, AutocompleteInput } from 'react-admin';
const UserCountry = () => {
const { data, isPending } = useGetList('countries');
// data is an array of { id: 123, code: 'FR', name: 'France' }
return (
<AutocompleteInput
source="country"
choices={data}
optionText="name"
optionValue="code"
isPending={isPending}
/>
);
}
offline
<AutocompleteInput> can display a custom message when it can’t fetch the choices because there is no network connectivity, thanks to the offline prop.
<ReferenceInput source="user_id" reference="users">
<AutocompleteInput offline={<span>No network, could not fetch data</span>} />
</ReferenceInput>
You can pass either a React element or a string to the offline prop:
<ReferenceInput source="user_id" reference="users">
<AutocompleteInput offline={<span>No network, could not fetch data</span>} />
</ReferenceInput>
<ReferenceInput source="user_id" reference="users">
<AutocompleteInput offline="No network, could not fetch data" />
</ReferenceInput>
onChange
Use the onChange prop to get notified when the input value changes.
Its value must be a function, defined as follows:
type OnChange = (
value: any, // the new value
record: RaRecord // the selected record
) => void;
In the following example, the onChange prop is used to update the language field whenever the user selects a new author:
import * as React from 'react';
import {
AutocompleteInput,
AutocompleteInputProps,
Create,
ReferenceInput,
SimpleForm,
TextInput,
} from 'react-admin';
import { useFormContext } from 'react-hook-form';
const LanguageChangingAuthorInput = () => {
const { setValue } = useFormContext();
const handleChange: AutocompleteInputProps['onChange'] = (
value,
record
) => {
// handleChange will be called with, for instance:
// value: 2,
// record: { id: 2, name: 'Victor Hugo', language: 'French' }
setValue('language', record?.language);
};
return (
<ReferenceInput reference="authors" source="author">
<AutocompleteInput optionText="name" onChange={handleChange} />
</ReferenceInput>
);
};
const BookCreate = () => (
<Create
mutationOptions={{
onSuccess: data => {
console.log(data);
},
}}
redirect={false}
>
<SimpleForm>
<LanguageChangingAuthorInput />
<TextInput source="language" />
</SimpleForm>
</Create>
);
onCreate
Use the onCreate prop to allow users to create new options on the fly. This is equivalent to MUI’s <AutoComplete freeSolo> prop.
onCreate must be a function that adds a new choice and returns it. This function can be async. The added choice must use the same format as the other choices (usually { id, name }).
In the following example, users can create a new company by typing its name in the <AutocompleteInput>:
import { AutocompleteInput, Create, SimpleForm, TextInput } from 'react-admin';
const ContactCreate = () => {
const companies = [
{ id: 1, name: 'Globex Corp.' },
{ id: 2, name: 'Soylent Inc.' },
];
return (
<Create>
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="first_name" />
<TextInput source="last_name" />
<AutocompleteInput
source="company"
choices={companies}
onCreate={companyName => {
const newCompany = { id: companies.length + 1, name: companyName };
companies.push(newCompany);
return newCompany;
}}
/>
</SimpleForm>
</Create>
);
}
If you want to customize the label of the “Create XXX” option, use the createItemLabel prop.
When used inside a <ReferenceInput>, the onCreate prop should create a new record in the reference resource, and return it. See Creating a New Reference for more details.
If a function is not enough, you can use the create prop to render a custom component instead.
optionText
By default, <AutocompleteInput> uses the name property as the text content of each option.
import { AutocompleteInput } from 'react-admin';
<AutocompleteInput
source="category"
choices={[
{ id: 'tech', name: 'Tech' },
{ id: 'lifestyle', name: 'Lifestyle' },
{ id: 'people', name: 'People' },
]}
/>
// renders the following list of choices
// - Tech
// - Lifestyle
// - People
If your choices don’t have a name property, or if you want to use another property, you can use the optionText prop to specify which property to use:
<AutocompleteInput
source="category"
optionText="label"
choices={[
{ id: 'tech', label: 'Tech' },
{ id: 'lifestyle', label: 'Lifestyle' },
{ id: 'people', label: 'People' },
]}
/>
optionText also accepts a function, so you can shape the option text at will:
const choices = [
{ id: 123, first_name: 'Leo', last_name: 'Tolstoi' },
{ id: 456, first_name: 'Jane', last_name: 'Austen' },
];
// Note we declared the function outside the component to avoid rerenders
const optionRenderer = choice => `${choice.first_name} ${choice.last_name}`;
<AutocompleteInput source="author_id" choices={choices} optionText={optionRenderer} />
Tip: Make sure you provide a stable reference to the function passed as optionText. Either declare it outside the component render function or wrap it inside a useCallback.
optionText also accepts a React Element, that will be rendered inside a <RecordContext> using the related choice as the record prop. You can use Field components there. However, using an element as optionText implies that you also set two more props, inputText and matchSuggestion. See Using A Custom Element For Options for more details.
optionText can also be useful when the choices are records fetched from another resource, and <AutocompleteInput> is a child of a <ReferenceInput>. In that case, react-admin uses the recordRepresentation of the related resource to display the record label. In the example below, <AutocompleteInput> renders author options via their last_name attribute, because it’s the record representation defined in the <Resource name="authors">:
// in src/PostCreate.jsx
import { AutocompleteInput, Create, ReferenceInput, SimpleForm } from 'react-admin';
export const PostCreate = () => (
<Create>
<SimpleForm>
<ReferenceInput label="Author" source="author_id" reference="authors">
<AutocompleteInput />
</ReferenceInput>
</SimpleForm>
</Create>
);
// in src/App.js
import { Admin, Resource, ListGuesser } from 'react-admin';
import { dataProvider } from './dataProvider';
import { PostCreate } from './PostCreate';
export const App = () => (
<Admin dataProvider={dataProvider}>
<Resource name="posts" list={ListGuesser} create={PostCreate} />
<Resource name="authors" recordRepresentation="last_name" />
</Admin>
)
If you set the optionText prop, react-admin uses it instead of relying on recordRepresentation:
// in src/PostCreate.jsx
import { AutocompleteInput, Create, ReferenceInput, SimpleForm } from 'react-admin';
export const PostCreate = () => (
<Create>
<SimpleForm>
<ReferenceInput label="Author" source="author_id" reference="authors">
<AutocompleteInput optionText={author => `${author.first_name} ${author.last_name}`} />
</ReferenceInput>
</SimpleForm>
</Create>
);
Now <AutocompleteInput> will render author options using their full name.
optionValue
You can customize the property to use for the option value (instead of the default id) thanks to the optionValue prop:
const choices = [
{ _id: 'tech', name: 'Tech' },
{ _id: 'lifestyle', name: 'Lifestyle' },
{ _id: 'people', name: 'People' },
];
<AutocompleteInput
source="category"
choices={choices}
optionValue="_id"
/>
Note: optionValue is only supported when the choices are provided directly via the choices prop. If you use <AutocompleteInput> inside a <ReferenceInput>, the optionValue is always set to id, as the choices are records fetched from the related resource, and records should always have an id field.
shouldRenderSuggestions
When dealing with a large amount of choices you may need to limit the number of suggestions that are rendered in order to maintain acceptable performance. shouldRenderSuggestions is an optional prop that allows you to set conditions on when to render suggestions. An easy way to improve performance would be to skip rendering until the user has entered 2 or 3 characters in the search box. This lowers the result set significantly and might be all you need (depending on your data set).
<AutocompleteInput
source="category"
choices={choices}
shouldRenderSuggestions={(val) => { return val.trim().length > 2 }}
/>
suggestionLimit
The choices prop can be very large, and rendering all of them would be very slow. To limit the number of suggestions displayed at any time, set the suggestionLimit prop:
<AutocompleteInput
source="category"
choices={choices}
suggestionLimit={10}
/>
If you’re using <AutocompleteInput> inside a <ReferenceInput>, limit the number of choices returned by the API instead, using the perPage prop of the <ReferenceInput>.
<ReferenceInput label="Author" source="author_id" reference="authors" perPage={10}>
<AutocompleteInput />
</ReferenceInput>
sx: CSS API
The <AutocompleteInput> component accepts the usual className prop. You can also override many styles of the inner components thanks to the sx property (see the sx documentation for syntax and examples). This property accepts the following subclasses:
| Rule name | Description |
|---|---|
& .RaSelectInput-textField |
Applied to the underlying TextField component |
To override the style of all instances of <AutocompleteInput> using the application-wide style overrides, use the RaAutocompleteInput key.
Refer to the Material UI <Autocomplete> component to know its CSS API.
translateChoice
The choices are translated by default, so you can use translation identifiers as choices:
const choices = [
{ id: 'M', name: 'myroot.gender.male' },
{ id: 'F', name: 'myroot.gender.female' },
];
However, in some cases (e.g. inside a <ReferenceInput>), you may not want the choice to be translated.
In that case, set the translateChoice prop to false.
<AutocompleteInput source="gender" choices={choices} translateChoice={false}/>
Additional Props
<AutocompleteInput> renders a Material UI <Autocomplete> component and it accepts the <Autocomplete> props:
<AutocompleteInput source="category" size="large" />
Fetching Choices
You can use useGetList to fetch choices. For example, to fetch a list of countries for a user profile:
import { useGetList, AutocompleteInput } from 'react-admin';
const CountryInput = () => {
const { data, isPending } = useGetList('countries');
// data is an array of { id: 123, code: 'FR', name: 'France' }
return (
<AutocompleteInput
source="country"
choices={data}
optionText="name"
optionValue="code"
isPending={isPending}
/>
);
}
The isPending prop is used to display a loading indicator while the data is being fetched.
However, most of the time, if you need to populate a <AutocompleteInput> with choices fetched from another resource, it’s because you are trying to set a foreign key. In that case, you should use <ReferenceInput> to fetch the choices instead (see next section).
Selecting a Foreign Key
If you use <AutocompleteInput> to set a foreign key for a many-to-one or a one-to-one relationship, you’ll have to fetch choices, as explained in the previous section. You’ll also have to fetch the record corresponding to the current value of the foreign key, as it may not be in the list of choices.
For example, if a contact has one company via the company_id foreign key, a contact form can let users select a company as follows:
import { useState } from 'react';
import { useGetList, useGetOne, AutocompleteInput } from 'react-admin';
import { useWatch } from 'react-hook-form';
const CompanyInput = () => {
const [filter, setFilter] = useState({ q: '' });
// fetch possible companies
const { data: choices, isPending: isPendingChoices } = useGetList('companies', { filter });
// companies are like { id: 123, name: 'Acme' }
// get the current value of the foreign key
const companyId = useWatch({ name: 'company_id'})
// fetch the current company
const { data: currentCompany, isPending: isPendingCurrentCompany } = useGetOne('companies', { id: companyId });
// if the current company is not in the list of possible companies, add it
const choicesWithCurrentCompany = choices
? choices.find(choice => choice.id === companyId)
? choices
: [...choices, currentCompany]
: [];
const isPending = isPendingChoices && isPendingCurrentCompany;
return (
<AutocompleteInput
label="Company"
source="company_id"
choices={choicesWithCurrentCompany}
optionText="name"
disabled={isPending}
onInputChange={e => setFilter({ q: e.target.value })}
/>
);
}
As this is a common task, react-admin provides a shortcut to do the same in a declarative way: <ReferenceInput>:
import { ReferenceInput, AutocompleteInput, required } from 'react-admin';
const CompanyInput = () => (
<ReferenceInput reference="companies" source="company_id">
<AutocompleteInput
label="Company"
source="company_id"
optionText="name"
validate={required()}
/>
</ReferenceInput>
);
Tip: If you need validation (e.g. required()), put the validate prop on the child input (<AutocompleteInput>). <ReferenceInput> doesn’t accept validation props.
<ReferenceInput> is a headless component that:
- fetches a list of records with
dataProvider.getList()anddataProvider.getOne(), using thereferenceprop for the resource, - puts the result of the fetch in the
ChoiceContextas thechoicesprop, as well as theisPendingstate, - and renders its child component
When rendered as a child of <ReferenceInput>, <AutocompleteInput> reads that ChoiceContext to populate its own choices and isPending props. It also sends the current input prop to the useGetList hook, so that the list of choices is filtered as the user types.
In fact, you can simplify the code even further:
<ReferenceInput>puts all its props inside theChoiceContext, includingsource, so<AutocompleteInput>doesn’t need to repeat it.- You can also put the
labelprop on the<ReferenceInput>rather than<AutocompleteInput>so that it looks just like<ReferenceField>(for easier memorization). <AutocompleteInput>uses therecordRepresentationto determine how to represent the related choices. In the example above, thecompaniesresource usesnameas itsrecordRepresentation, so<AutocompleteInput>will default tooptionText="name".<ReferenceInput>’s default child is<AutocompleteInput>, so you can omit it entirely.
The code for the <CompanyInput> component can be reduced to:
import { ReferenceInput } from 'react-admin';
const CompanyInput = () => (
<ReferenceInput reference="companies" source="company_id" label="Company" />
);
This is the recommended approach for using <AutocompleteInput> to select a foreign key. This not only signifies that the input is a <AutocompleteInput> but also highlights its function in fetching choices from another resource, ultimately enhancing the code’s readability.
Tip: <ReferenceInput> is much more powerful than the initial snippet. It optimizes and caches API calls, enables refetching of both API calls with a single command, and stores supplementary data in the <ChoicesContext>. <ReferenceInput> can provide choices to <AutocompleteInput>, but also to <RadioButtonGroupInput> and <SelectInput>. For further information, refer to the <ReferenceInput> documentation.
<AutocompleteInput> uses the filterToQuery prop to determine how to map the input string into a filter. You may want to customize that function to match the filtering capabilities of your API:
const filterToQuery = searchText => ({ name_ilike: `%${searchText}%` });
<ReferenceInput reference="companies" source="company_id" label="Company">
<AutocompleteInput filterToQuery={filterToQuery} />
</ReferenceInput>
Also, <ReferenceInput> doesn’t call dataProvider.getList() on every keystroke. It waits for the user to stop typing for 250ms before calling the API. You can customize this delay using the debounce prop:
<ReferenceInput reference="companies" source="company_id" label="Company">
<AutocompleteInput debounce={500} />
</ReferenceInput>
Using A Custom Element For Options
You can pass a custom element as optionText to have <AutocompleteInput> render each suggestion in a custom way.
<AutocompleteInput> will render the custom option element inside a <RecordContext>, using the related choice as the record prop. You can use Field components there.
However, as the underlying Material UI <Autocomplete> component requires that the current selection is a string, you must also pass a function as the inputText prop. This function should return a text representation of the current selection. You should also pass a matchSuggestion function to filter the choices based on the current selection.
const choices = [
{ id: 123, first_name: 'Leo', last_name: 'Tolstoi', avatar:'/penguin' },
{ id: 456, first_name: 'Jane', last_name: 'Austen', avatar:'/panda' },
];
const OptionRenderer = () => {
const record = useRecordContext();
return (
<span>
<img src={record.avatar} />
{record.first_name} {record.last_name}
</span>
);
};
const optionText = <OptionRenderer />;
const inputText = choice => `${choice.first_name} ${choice.last_name}`;
const matchSuggestion = (filter, choice) => {
return (
choice.first_name.toLowerCase().includes(filter.toLowerCase())
|| choice.last_name.toLowerCase().includes(filter.toLowerCase())
);
};
<AutocompleteInput
source="author_id"
choices={choices}
optionText={optionText}
inputText={inputText}
matchSuggestion={matchSuggestion}
/>
Tip: Make sure you pass stable references to the functions passed to the inputText and matchSuggestion by either declaring them outside the component render function or by wrapping them in a useCallback.
Tip: Make sure you pass a stable reference to the element passed to the optionText prop by calling it outside the component render function like so:
const OptionRenderer = () => {
const record = useRecordContext();
return (
<span>
<img src={record.avatar} />
{record.first_name} {record.last_name}
</span>
);
};
const optionText = <OptionRenderer />;
Creating New Choices
The <AutocompleteInput> can allow users to create a new choice if either the create or onCreate prop is provided.
Use the onCreate prop when you only require users to provide a simple string and a prompt is enough. You can return either the new choice directly or a Promise resolving to the new choice.
import { AutocompleteInput, Create, SimpleForm, TextInput } from 'react-admin';
const PostCreate = () => {
const categories = [
{ name: 'Tech', id: 'tech' },
{ name: 'Lifestyle', id: 'lifestyle' },
];
return (
<Create>
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="title" />
<AutocompleteInput
onCreate={(filter) => {
const newCategoryName = window.prompt('Enter a new category', filter);
const newCategory = { id: categories.length + 1, name: newCategoryName };
categories.push(newCategory);
return newCategory;
}}
source="category"
choices={categories}
/>
</SimpleForm>
</Create>
);
}
Use the create prop when you want a more polished or complex UI. For example a Material UI <Dialog> asking for multiple fields because the choices are from a referenced resource.
import {
AutocompleteInput,
Create,
CreateBase,
ReferenceInput,
SimpleForm,
TextInput,
useCreateSuggestionContext,
} from 'react-admin';
import CloseIcon from '@mui/icons-material/Close';
import {
Dialog,
DialogContent,
DialogTitle,
IconButton,
} from '@mui/material';
const PostCreate = () => {
return (
<Create>
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="title" />
<ReferenceInput source="category_id" reference="categories">
<AutocompleteInput create={<CreateCategory />} />
</ReferenceInput>
</SimpleForm>
</Create>
);
}
const CreateCategory = () => {
const { filter, onCancel, onCreate } = useCreateSuggestionContext();
return (
<Dialog open onClose={onCancel}>
<DialogTitle sx={{ m: 0, p: 2 }}>Create Category</DialogTitle>
<IconButton
aria-label="close"
onClick={onCancel}
sx={theme => ({
position: 'absolute',
right: 8,
top: 8,
color: theme.palette.grey[500],
})}
>
<CloseIcon />
</IconButton>
<DialogContent sx={{ p: 0 }}>
<CreateBase
redirect={false}
resource="categories"
mutationOptions={{
onSuccess: onCreate,
}}
>
<SimpleForm defaultValues={{ title: filter }}>
<TextInput source="name" helperText={false} autoFocus/>
</SimpleForm>
</CreateBase>
</DialogContent>
</Dialog>
);
};
Tip: As showcased in this example, react-admin provides a convenient hook for accessing the filter the user has already input in the <AutocompleteInput>: useCreateSuggestionContext.
The Create %{item} option will only be displayed once the user has already set a filter (by typing in some input). If you expect your users to create new items often, you can make this more user-friendly by adding a placeholder text like this:
const PostCreate = () => {
const categories = [
{ name: 'Tech', id: 'tech' },
{ name: 'Lifestyle', id: 'lifestyle' },
];
return (
<Create>
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="title" />
<AutocompleteInput
onCreate={(filter) => {
const newCategoryName = window.prompt('Enter a new category', filter);
const newCategory = { id: categories.length + 1, name: newCategoryName };
categories.push(newCategory);
return newCategory;
}}
source="category"
choices={categories}
+ TextFieldProps={{
+ placeholder: 'Start typing to create a new item',
+ }}
/>
</SimpleForm>
</Create>
);
}

