<ArrayInput>
To edit arrays of data embedded inside a record, <ArrayInput> creates a list of sub-forms.
Usage
<ArrayInput> allows editing of embedded arrays, like the items field in the following order record:
{
"id": 1,
"date": "2022-08-30",
"customer": "John Doe",
"items": [
{
"name": "Office Jeans",
"price": 45.99,
"quantity": 1,
},
{
"name": "Black Elegance Jeans",
"price": 69.99,
"quantity": 2,
},
{
"name": "Slim Fit Jeans",
"price": 55.99,
"quantity": 1,
},
],
}
Tip: If you need to edit an array of strings, like a list of email addresses or a list of tags, you should use a <TextArrayInput> instead.
<ArrayInput> expects a single child, which must be a form iterator component. A form iterator is a component rendering a field array (the object returned by react-hook-form’s useFieldArray). For instance, the <SimpleFormIterator> component displays an array of react-admin Inputs in an unordered list (<ul>), one sub-form by list item (<li>). It also provides controls for adding and removing a sub-record.
import {
Edit,
SimpleForm,
TextInput,
DateInput,
ArrayInput,
NumberInput,
SimpleFormIterator
} from 'react-admin';
const OrderEdit = () => (
<Edit>
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="customer" />
<DateInput source="date" />
<ArrayInput source="items">
<SimpleFormIterator inline>
<TextInput source="name" helperText={false} />
<NumberInput source="price" helperText={false} />
<NumberInput source="quantity" helperText={false} />
</SimpleFormIterator>
</ArrayInput>
</SimpleForm>
</Edit>
);
Check the <SimpleFormIterator> documentation for details about how to customize the sub form layout.
Tip: If you need to edit an array of related records, i.e. if the items above actually come from another resource, you should use a <ReferenceManyInput> instead.
Note: Using shouldUnregister should be avoided when using <ArrayInput> (which internally uses useFieldArray) as the unregister function gets called after input unmount/remount and reorder. This limitation is mentioned in the react-hook-form documentation. If you are in such a situation, you can use the transform prop to manually clean the submitted values.
Props
<ArrayInput> accepts the common input props (except disabled, readOnly, format and parse).
Global validation
If you are using an <ArrayInput> inside a form with global validation, you need to shape the errors object returned by the validate function like an array too.
For instance, to display the following errors:
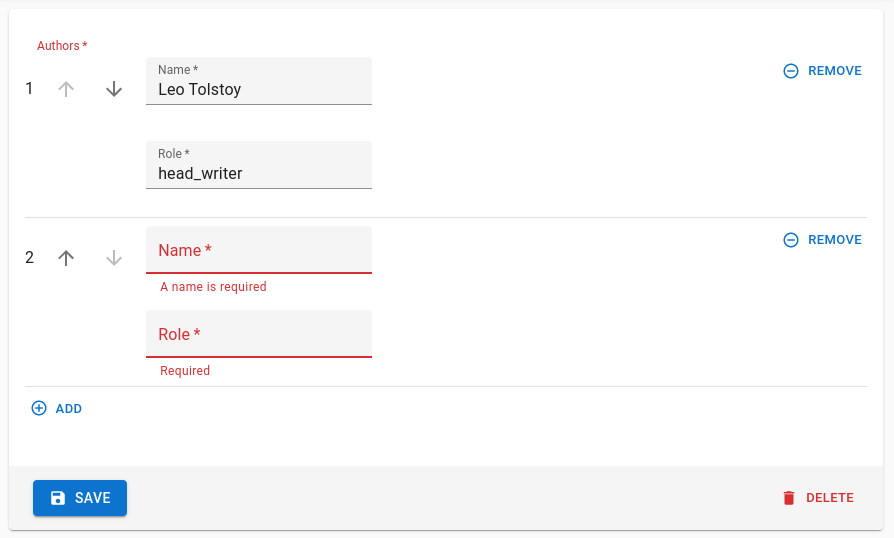
You need to return an errors object shaped like this:
{
authors: [
{},
{
name: 'A name is required',
role: 'ra.validation.required' // translation keys are supported too
},
],
}
Tip: You can find a sample validate function that handles arrays in the Form Validation documentation.
Disabling The Input
<ArrayInput> does not support the disabled and readOnly props.
If you need to disable the input, set the <SimpleFormIterator disabled> prop, and make the child inputs readOnly:
const OrderEdit = () => (
<Edit>
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="customer" />
<DateInput source="date" />
<ArrayInput source="items">
<SimpleFormIterator inline disabled>
<TextInput source="name" readOnly/>
<NumberInput source="price" readOnly />
<NumberInput source="quantity" readOnly />
</SimpleFormIterator>
</ArrayInput>
</SimpleForm>
</Edit>
);
Changing An Item’s Value Programmatically
You can leverage react-hook-form’s setValue method to change an item’s value programmatically.
However you need to know the name under which the input was registered in the form, and this name is dynamically generated depending on the index of the item in the array.
To get the name of the input for a given index, you can leverage the SourceContext created by react-admin, which can be accessed using the useSourceContext hook.
This context provides a getSource function that returns the effective source for an input in the current context, which you can use as input name for setValue.
Here is an example where we leverage getSource and setValue to change the role of an user to ‘admin’ when the ‘Make Admin’ button is clicked:
import { ArrayInput, SimpleFormIterator, TextInput, useSourceContext } from 'react-admin';
import { useFormContext } from 'react-hook-form';
import { Button } from '@mui/material';
const MakeAdminButton = () => {
const sourceContext = useSourceContext();
const { setValue } = useFormContext();
const onClick = () => {
// sourceContext.getSource('role') will for instance return
// 'users.0.role'
setValue(sourceContext.getSource('role'), 'admin');
};
return (
<Button onClick={onClick} size="small" sx={{ minWidth: 120 }}>
Make admin
</Button>
);
};
const UserArray = () => (
<ArrayInput source="users">
<SimpleFormIterator inline>
<TextInput source="name" helperText={false} />
<TextInput source="role" helperText={false} />
<MakeAdminButton />
</SimpleFormIterator>
</ArrayInput>
);
Tip: If you only need the item’s index, you can leverage the useSimpleFormIteratorItem hook instead.

